 PDF(13752 KB)
PDF(13752 KB)


Analysis on the Cause of Cold and Warm Transition in Beijing- Tianjin-Hebei during November-December 2022
Xuxu GAO, Shaojing CHE, Haoyu DU
 PDF(13752 KB)
PDF(13752 KB)
Analysis on the Cause of Cold and Warm Transition in Beijing- Tianjin-Hebei during November-December 2022
During November-December of 2022, the climate of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) showed significant cold and warm transition, and the average air temperature difference between November and December was 10.6 °C, ranked first with 1971 and 1980 since 1961.Based on NCEP/NCAR reanalysis and multiple climate index data, the possible causes of the air temperature transition in November and December 2022 in BTH was explored from the perspective of the interdecadal influence of atmospheric circulation transition, ENSO and AO on variation of temperature anomalies.The results show that the weak strength of the Ural Mountains Blocking High and the Siberian High, as well as the strong strength of the Western Pacific Subtropical high led to the abnormally warm climate in the BTH region in November.But the turning of the atmospheric circulation in December, the strengthening of the Ural Blocking high, the deepening of the East Asia Great trough, the strengthening of the Siberian high, and the northerly air flow in BTH, resulting in the abnormally cold December.The temperature anomaly difference of these two months showed obvious interdecadal changes, positive in 1961-1985, negative in 1986 -2003, and positive again in 2004 -2022.Compared to the cold and warm transition events in 1971, 1980, and 2005, there were interdecadal changes observed in atmospheric circulation transitions.The weak cold air activity in the north and the southern warm air flow influenced by the strengthening of the Western Pacific subtropical high acted together to cause the warm November of 2022 and 2005.However, the weak cold air activity in the north was mainly influence factor for warm November 1971 and 1980.The combination of significant Arctic warming and a significantly stronger Siberian high led to unusually cold Decembers in 2022 and 2005.The correlation between ENSO and November temperature in the BTH, as well as the correlation between AO and December temperature, exhibited a significant increase during the 2000s.In the context of La Nin ̃a, AO transitioned from a positive phase in November to a negative phase in December, resulting in a high likelihood of temperature inversion.Given that 2022 was the year of La Niña and influenced by an AO shift, a cold to warm transition event occurred in the BTH from November to December.
transition from warm to cold / Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei / ENSO / AO {{custom_keyword}} /
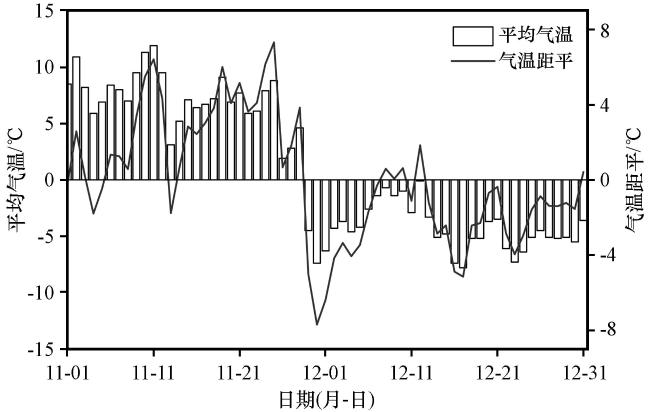
Fig.1 Daily variation of mean temperature and its anomalies in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from November to December in 2022图1 2022年11 -12月京津冀地区日平均气温及距平变化 |
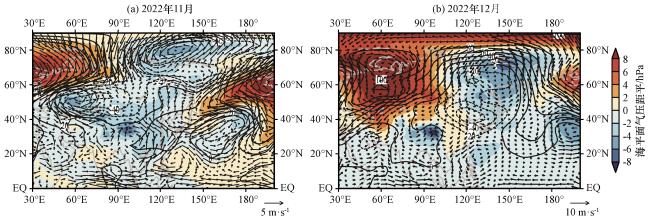
Fig.4 The sea surface pressure anomalies (color area, unit: hPa), 500 hPa geopotential height anomalies (contour, unit: gpm) and 850 hPa wind anomalies (vector, unit: m·s-1) for November (a) and December (b) in 2022图4 2022年11月(a)和12月(b)的海平面气压距平(彩色区, 单位: hPa)、 500 hPa位势高度距平 (等值线, 单位: gpm)和850 hPa风场距平(矢量, 单位: m·s-1) |
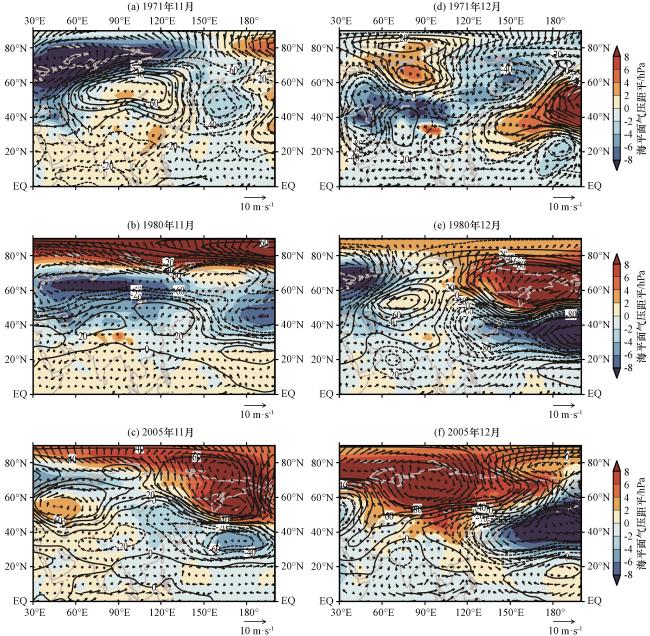
Fig.5 Sea surface pressure anomalies (color area, unit: hPa), 500 hPa geopotential height anomalies (contour, unit: gpm), and 850 hPa wind anomalies (vector, unit: m·s-1).In Fig.5, (a)~(c) for November in 1971, 1980, and 2005, (d)~(f) for December in 1971, 1980, and 2005图5 海平面气压距平(彩色区, 单位: hPa)、 500 hPa位势高度距平(等值线, 单位: gpm)和850 hPa风场距平(矢量, 单位: m·s-1) (a)~(c)分别为1971年、 1980年、 2005年的11月; (d)~(f)分别为1971年、 1980年、 2005年的12月 |
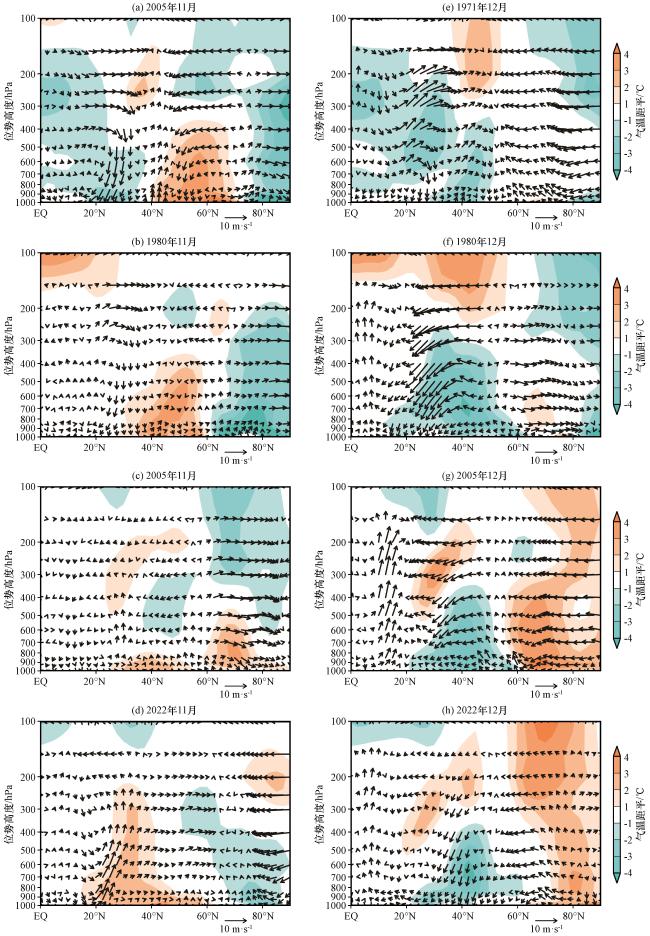
Fig.6 Mean air temperature anomaly (color area, unit: ° C) and meridional circulation (vector, unit: m·s-1, vertical velocity expanded by 100 times) latitudinal altitude profile in 113°E -120°E area.In Fig.6, (a)~(d) for November in 1971, 1980, 2005, and 2022, (e)~(h) for December in 1971, 1980, 2005, and 2022图6 113°E -120°E 范围平均气温距平(彩色区, 单位: ℃)和经向环流(矢量, 单位: m·s-1, 垂直速度扩大100倍) 纬度-高度剖面(a)~(d)分别为1971年、 1980年、 2005年、 2022年的11月; (e)~(h)分别为1971年、 1980年、 2005年、 2022的12月 |
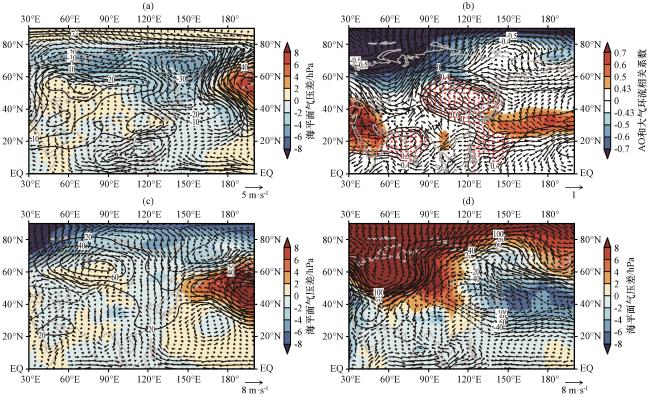
Fig.9 The differences (La |
Table 1 AO indies and temperature anomalies in November and December La Ni |
| La | 11月AO 指数 | 12月AO 指数 | 11月气温 距平 | 12月气温 距平 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 0.2277 | -2.1039 | 2.1 | -1.7 |
| 2007 | -0.5187 | 0.8211 | 0.0 | 1.4 |
| 2010 | -0.3757 | -2.6310 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| 2011 | 1.4592 | 2.2208 | 1.5 | -0.6 |
| 2017 | -0.0776 | -0.0590 | -0.7 | 0.6 |
| 2020 | 2.0864 | -1.736 | 0.7 | -1.6 |
| 2021 | 0.0930 | 0.1981 | 0.9 | 2.0 |
| 2022 | 0.3389 | -2.7192 | 1.9 | -2.0 |
| 加粗字体表示AO由11月正位相转为12月负位相的拉尼娜年(The bold font indicates La Niña years in which the AO changes from positive phase in November to negative phase in December) |
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
车少静, 王冀, 李晓帆, 等, 2022.京津冀后冬极端低温与北极涛动相关性年代际减弱[J].气象, 48(4): 418-427.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
陈文, 兰晓青, 王林, 等, 2013.ENSO和北极涛动对东亚冬季气候异常的综合影响[J].科学通报, 58(8): 634-641.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
韩笑笑, 孟宪红, 赵林, 等, 2023.“北极放大”现象驱动因素及其影响的研究进展综述[J].高原气象, 42(1): 1-12.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2022.00029.Han X X ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
郝立生, 何丽烨, 马宁, 等, 2023.厄尔尼诺事件年际变化与我国华北夏季干旱的关系[J].干旱气象, 41(6): 829-840.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-06-0829.Hao L S ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
蒋薇, 张祖强, 刘芸芸, 2016.21世纪以来西南地区干季降水与西太平洋副热带高压年代际变化的关系[J].气象, 42(11): 1335-1341.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
琚建华, 任菊章, 2005.冬季太平洋海温的年代际变化对亚洲地表气温异常的影响[J].气象科学, 25(1): 18-25.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
蓝柳茹, 李栋梁, 2016.西伯利亚高压的年际和年代际异常特征及其对中国冬季气温的影响[J].高原气象, 35(3): 662-674.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2016.00022.Lan L R ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
梁阔, 李丽平, 任景华, 等, 2023.中纬度海温对北方冬季寒潮强度异常的协同影响[J].高原气象, 42(3): 711-724.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2022.00095.Liang K ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
李琳, 李崇银, 谭言科, 等, 2010.平流层爆发性增温对中国天气气候的影响及其在ENSO影响中的作用[J].地球物理学报, 53(7): 1529-1542.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.07004.Li L ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
李维京, 李怡, 陈丽娟, 等, 2013.我国冬季气温与影响因子关系的年代际变化[J].应用气象学报, 24(4): 385-396.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
庞子琴, 郭品文, 2010.不同年代际背景下AO与冬季中国东北气温的关系[J].大气科学学报, 33(4): 469-476.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
祁莉, 泮琬楠, 2021.东亚气温前冬与后冬反相的变化特征及可能影响因子[J].大气科学, 45(5): 1039-1056.DOI: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2011.20181.Qi L ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
乔少博, 张志森, 孙晓娟, 等, 2015.晚秋和后冬间欧亚遥相关型波列反相现象探究[J].气象学报, 73(4): 711-724.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
孙健, 李栋梁, 邵鹏程, 等, 2019.中国冬季气温月际变化特征及其对大气环流异常的响应[J].气象学报, 77(5): 885-897.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
谭赢, 李丽平, 施春华, 等, 2022.中国冬季大范围持续性低温事件低频特征及其与大气低频振荡的联系[J].高原气象, 41(6): 1410-1424.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2021.00118.Tan Y ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
王婧, 吕俊梅, 2021.“暖北极-冷欧亚”模态的年代际变化及其与北大西洋海温的联系[J].大气科学, 45(4): 915-930.DOI: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2103.20205.Wang J ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
韦玮, 王林, 陈权亮, 等, 2014.我国前冬和后冬气温年际变化的特征与联系 [J].大气科学, 38(3): 524-536.DOI: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1401.13320.Wei W ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
伍红雨, 潘蔚娟, 王婷, 2014.华南冬季气温异常与ENSO的关系[J].气象, 40(10): 1230-1239.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
徐彬羽, 姚素香, 孙庆飞, 2023.冬季乌拉尔山阻塞高压建立和维持与位势高度季节内振荡的联系[J].高原气象, 42(6): 1548-1561.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2023.00006.Xu B Y ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
杨光, 李崇银, 李琳, 2012.平流层爆发性增温及其影响研究进展[J].气象科学, 32(6): 694-708.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
张向东, 傅云飞, 管兆勇, 等, 2020.北极增幅性变暖对欧亚大陆冬季极端天气和气候的影响: 共识、 问题和争议[J].气象科学, 40(5): 596-604.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
朱益民, 杨修群, 陈晓颖, 等, 2007.ENSO与中国夏季年际气候异常关系的年代际变化[J].热带气象学报, 23(2): 105-116.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 PDF(13752 KB)
PDF(13752 KB)
 Fig.1 Daily variation of mean temperature and its anomalies in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from November to December in 2022
Fig.1 Daily variation of mean temperature and its anomalies in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from November to December in 2022 Fig.2 The temperature anomalies in November and December and anomaly difference between these two months in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1961 to 2022
Fig.2 The temperature anomalies in November and December and anomaly difference between these two months in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1961 to 2022 Fig.3 Spatial distribution of temperature anomaly difference (unit: ℃) between November and December in three ages.(a) from 1961 to 1985, (b) from 1986 to 2003, (c) form 2004 to 2022
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of temperature anomaly difference (unit: ℃) between November and December in three ages.(a) from 1961 to 1985, (b) from 1986 to 2003, (c) form 2004 to 2022 Fig.4 The sea surface pressure anomalies (color area, unit: hPa), 500 hPa geopotential height anomalies (contour, unit: gpm) and 850 hPa wind anomalies (vector, unit: m·s-1) for November (a) and December (b) in 2022
Fig.4 The sea surface pressure anomalies (color area, unit: hPa), 500 hPa geopotential height anomalies (contour, unit: gpm) and 850 hPa wind anomalies (vector, unit: m·s-1) for November (a) and December (b) in 2022 Fig.5 Sea surface pressure anomalies (color area, unit: hPa), 500 hPa geopotential height anomalies (contour, unit: gpm), and 850 hPa wind anomalies (vector, unit: m·s-1).In Fig.5, (a)~(c) for November in 1971, 1980, and 2005, (d)~(f) for December in 1971, 1980, and 2005
Fig.5 Sea surface pressure anomalies (color area, unit: hPa), 500 hPa geopotential height anomalies (contour, unit: gpm), and 850 hPa wind anomalies (vector, unit: m·s-1).In Fig.5, (a)~(c) for November in 1971, 1980, and 2005, (d)~(f) for December in 1971, 1980, and 2005 Fig.6 Mean air temperature anomaly (color area, unit: ° C) and meridional circulation (vector, unit: m·s-1, vertical velocity expanded by 100 times) latitudinal altitude profile in 113°E -120°E area.In Fig.6, (a)~(d) for November in 1971, 1980, 2005, and 2022, (e)~(h) for December in 1971, 1980, 2005, and 2022
Fig.6 Mean air temperature anomaly (color area, unit: ° C) and meridional circulation (vector, unit: m·s-1, vertical velocity expanded by 100 times) latitudinal altitude profile in 113°E -120°E area.In Fig.6, (a)~(d) for November in 1971, 1980, 2005, and 2022, (e)~(h) for December in 1971, 1980, 2005, and 2022 Fig.7 The WACE index and 11-year moving average during December from 1961 to 2022
Fig.7 The WACE index and 11-year moving average during December from 1961 to 2022 Fig.8 Sliding correlations in a 21-year window between air temperature and Niño3.4 (a), between air temperature and AO index (b)
Fig.8 Sliding correlations in a 21-year window between air temperature and Niño3.4 (a), between air temperature and AO index (b) Fig.9 The differences (La N i n ˜ a years results minus El N i n ˜ o years results) of atmospheric circulation in November (a), the correlation coefficient between AO and air circulation in December(b), the atmospheric circulation difference in November (c) and December (d) during 2001 to 2022.In Fig.9 (a, d, d) the color area indicates sea surface pressure (unit: hPa), the contour indicates 500 hPa geopotential heigh (unit: gpm), the vector indicates the difference of 850 hPa wind field (unit: m·s-1).In Fig.9 (b), the doted area indicates geopotential heigh and AO have passed significance test at the 0.05 level
Fig.9 The differences (La N i n ˜ a years results minus El N i n ˜ o years results) of atmospheric circulation in November (a), the correlation coefficient between AO and air circulation in December(b), the atmospheric circulation difference in November (c) and December (d) during 2001 to 2022.In Fig.9 (a, d, d) the color area indicates sea surface pressure (unit: hPa), the contour indicates 500 hPa geopotential heigh (unit: gpm), the vector indicates the difference of 850 hPa wind field (unit: m·s-1).In Fig.9 (b), the doted area indicates geopotential heigh and AO have passed significance test at the 0.05 level Table 1 AO indies and temperature anomalies in November and December La Ni n ˜a years since 2001
Table 1 AO indies and temperature anomalies in November and December La Ni n ˜a years since 2001/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |