 PDF(4116 KB)
PDF(4116 KB)


Analysis of Precipitation Characteristics of Complex Terrain in Sichuan Province Based on Spatially Dense Rainfall Observation
Qiuxue ZHOU, Lan KANG, Keji LONG, Liangmin FENG
 PDF(4116 KB)
PDF(4116 KB)
Analysis of Precipitation Characteristics of Complex Terrain in Sichuan Province Based on Spatially Dense Rainfall Observation
Based on the hourly precipitation data of 3454 stations with dense space in Sichuan Province and the high-precision grid elevation data, the characteristics of precipitation in flood season in 7 regions of Sichuan Province in recent 10 years were analyzed.The results showed that: (1) There were 3 maximum centers of rainfall in flood season in Sichuan Province: Ya 'an in the southwest of the basin, Anxian in the northwest of the basin and Yanbian in the south of Panxi area.Anxian was the center of heavy rainstorm, and the rainfall in flood season was mainly contributed by the weather process of R 24 ≥100 mm.(2) Affected by the trend of the mountains and the steepness of the terrain, the morphology and isoline gradient of the large value area around the basin had obvious differences.And the larger the accumulated rainfall in flood season, the more the sites were concentrated on the windward slope of the mountains.(3) The degree of night rain gradually weakened from southwest to northeast, among which Panzhihua was the most significant area of night rain in flood season.(4)The daily distribution of R 24 ≥25 mm heavy rainfall was closely related to topography, and the heavy rainfall stations were only distributed in the steep transition zone between the western basin and the plateau.In addition, the percentage of stations with hourly rain intensity ≥50 mm·h-1 in the rainstorm days in the northwest of the basin was the highest.(5) Compared with persistent heavy rain, the site distribution of persistent heavy rain was more significantly affected by the windward slope topography.
Sichuan / heavy rainfall / steep terrain / night rain / flood season {{custom_keyword}} /
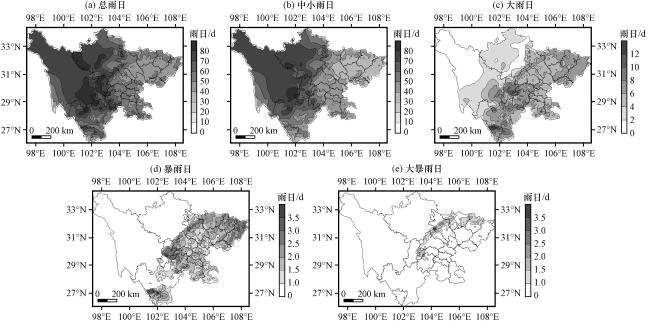
Fig.4 Distribution of average total rain days (a), small and moderate rain days (b), heavy rain days (c), rainstorm rain days (d) and large rainstorm rain days (e) during flood season in Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2022.Unit: d图4 2013 -2022年四川省平均汛期总雨日(a)、 中小雨日(b)、 大雨日(c)、 暴雨日(d)和大暴雨日(e)分布(单位: d) |
Table 1 Days of rainstorm and large rainstorm in different areas, the ratio of the maximum number of stations reaching the standard and the maximum daily rainfall表1 不同地区暴雨和大暴雨的日数、 最大达标站数比率和最大日雨量 |
| 暴雨 | 大暴雨 | 最大日雨量 /mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨日数/d | 最大达标站数比率/% | 雨日数/d | 最大达标站数比率/% | ||
| 盆地东北部(E区) | 55 | 44.9% | 25 | 30.8% | 510.3 |
| 盆地西北部(A区) | 62 | 42.7% | 26 | 51.7% | 750.6 |
| 盆地西南部(B区) | 51 | 44.7% | 21 | 37.4% | 429.2 |
| 攀西地区(G区) | 53 | 23.4% | 13 | 4.4% | 332.8 |
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
陈子凡, 王磊, 李谢辉, 等, 2022.西南地区极端降水时空变化特征及其与强 ENSO 事件的关系[J].高原气象, 41(3): 604-616.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2022.00004.Chen Z F ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
陈妙霖, 毛文书, 师春香, 等, 2022.1991-2020年西南湿季小时极端降水特征与区域差异[J].成都信息工程大学学报, 37(4): 435-441.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
傅抱璞, 1992.地形和海拔高度对降水的影响[J].地理学报, 47(4): 302-314.DOI: 10.11821/ xb199204002.Fu B P , 1992.The effect of terrain and elevation on precipitation[J].Acta Geographica Sinica, 47(4): 302-314.DOI: 10.11821/xb199204002 .
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
胡迪, 李跃清, 2015.青藏高原东侧四川地区夜雨时空变化特征[J].大气科学, 39(1): 161-179.DOI: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1405.13307.Hu D ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
卢萍, 宇如聪, 周天军, 2009.四川盆地西部暴雨对初始水汽条件敏感性的模拟研究[J].大气科学, 33(2): 241-250.DOI: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2009.02.04.Lu P ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
李跃清, 张琪, 2014.西南地区夏季云量与降水的关系特征分析[J].自然资源学报, 29(3): 441-453.DOI: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2014.03.008.Li Y Q ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
李跃清, 张晓春, 2011.“雅安天漏”研究进展[J].暴雨灾害, 30(4): 289-295.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
李川, 陈静, 何光碧, 2006.高原东侧陡峭地形对一次强降水天气过程的影响[J].高原气象, 25(3): 442-450.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
刘子堂, 李谢辉, 杨静坤, 2022.四川盆地极端降水事件时空变化特征及未来趋势分析[J].成都信息工程大学学报, 37(4): 456-463.DOI: 10.16836/j.cnki.jcuit.2022.04.015.Liu Z T ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
吕晶, 李跃清, 邹槟骏, 等, 2018.1959-2016年峨眉山和周边地区不同量级降水变化特征[J].干旱气象, 36(2): 243-255.
DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2018)-02-0243.L ü J,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
廖菲, 洪延超, 郑国光, 2007.地形对降水的影响研究概述[J]气象科技, 35(3): 309-316.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
马振锋, 彭骏, 高文良, 等, 2006.近40 年西南地区的气候变化事实[J].高原气象, 25(4): 633-642.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
彭贵康, 李志友, 柴复新, 1985.雅安地形与降水的气候特征[J].高原气象, 4(3): 230-240.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
任国玉, 吴虹, 陈正洪, 2000.我国降水变化趋势的空间特征[J].应用气象学报, 11(3): 322-330.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
沈程锋, 李国平, 2022.基于GPM 资料的四川盆地及周边地区夏季地形降水垂直结构研究[J].高原气象, 41(6): 1532-1543.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2021.0116.Shen C F ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
四川省气象局, 2014.四川天气预报手册[M].成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 66.
Sichuan Meteorological Bureau, 2014.Sichuan weather forecast manual[J].Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University Press, 66.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
王夫常, 宇如聪, 陈昊明, 等, 2011.我国西南部降水日变化特征分析[J].暴雨灾害, 30(2): 117-121.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
王敬诗, 蒋熹, 张夕迪, 2022.中国夜雨的时空变化特征研究[J].南京大学学报(自然科学), 58(5): 750-765.DOI: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2022.05.002.Wang J S ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
周长艳, 岑思弦, 李跃清, 等, 2011.四川省近50年降水的变化特征及影响[J].地理学报, 66(5): 619-630.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
周长艳, 李跃清, 彭俊, 2006.高原东侧川渝盆地降水与水资源特征及变化[J].大气科学, 30(6): 1217-1226.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
周长艳, 李跃清, 房静, 等, 2008.高原东侧川渝盆地东西部夏季降水及其大尺度环流特征[J].高原山地气象研究, 28(2): 1-9.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
周秋雪, 刘莹, 冯良敏, 等, 2015.2008-2012年四川强小时雨强的时空分布特征[J].高原气象, 34(5): 1261-1268.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2014.00070.Zhou Q X ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
周秋雪, 李跃清, 蒋兴文, 等, 2016.“雅安天漏”降水变化气候特征的分析[J].自然资源学报, 31(2): 343-353.DOI: 10.11849/zrzyxb.20141350.Zhou Q X ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
周秋雪, 康岚, 蒋兴文, 等, 2019.四川盆地边缘山地强降水与海拔的关系[J], 气象, 45(6): 811-819.DOI: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2019.06.007.Zhou Q X ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
周强, 李国平, 毛文书, 2013.川渝地区夏季降水与赤道印度洋海温的诊断分析[J].自然资源学报, 28(7): 1187-1195.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
朱艳峰, 宇如聪, 2003.川西地区夏季降水的年际变化特征及与大尺度环流的联系[J].大气科学, 27(6): 1045-1056.DOI: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2003.06.08.Zhu Y F ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
钟水新, 2020.地形对降水的影响机理及预报方法研究进展[J].高原气象, 39(5): 1122-1132.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2019.00083.Zhong S X , 2020.Advances in the study of the influencing mechanism and forecast methods for orographic precipitation[J].Plateau Meteorology, 39(5): 1122-1132.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2019.00083 .
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 PDF(4116 KB)
PDF(4116 KB)
 Fig.1 Distribution of 3454 stations in Sichuan Province.The color area is elevation (unit: m).A~G are 7 regious in Sichuan Basin
Fig.1 Distribution of 3454 stations in Sichuan Province.The color area is elevation (unit: m).A~G are 7 regious in Sichuan Basin Fig.2 Distribution of average total rainfall (a), heavy rainfall (b), rainstorm rainfall (c) and large rainstorm rainfall (d) during flood season in Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2022.Unit: mm
Fig.2 Distribution of average total rainfall (a), heavy rainfall (b), rainstorm rainfall (c) and large rainstorm rainfall (d) during flood season in Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2022.Unit: mm Fig.3 Night rainfall, day rainfall (unit: mm) and night rain ratio (unit: %) during flood season in different regions of Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2022
Fig.3 Night rainfall, day rainfall (unit: mm) and night rain ratio (unit: %) during flood season in different regions of Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2022 Fig.4 Distribution of average total rain days (a), small and moderate rain days (b), heavy rain days (c), rainstorm rain days (d) and large rainstorm rain days (e) during flood season in Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2022.Unit: d
Fig.4 Distribution of average total rain days (a), small and moderate rain days (b), heavy rain days (c), rainstorm rain days (d) and large rainstorm rain days (e) during flood season in Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2022.Unit: d Table 1 Days of rainstorm and large rainstorm in different areas, the ratio of the maximum number of stations reaching the standard and the maximum daily rainfall
Table 1 Days of rainstorm and large rainstorm in different areas, the ratio of the maximum number of stations reaching the standard and the maximum daily rainfall Fig.5 Distribution of stations with rainfall intensity of 50 mm·h-1 in rainstorm days in different regions.Stations with 98% Quantile High Frequency Days in Red, and the color area is elevation (unit: m)
Fig.5 Distribution of stations with rainfall intensity of 50 mm·h-1 in rainstorm days in different regions.Stations with 98% Quantile High Frequency Days in Red, and the color area is elevation (unit: m) Fig.6 Distribution of the longest continuous days of rainstorm in flood season from 2013 to 2022.Unit: d
Fig.6 Distribution of the longest continuous days of rainstorm in flood season from 2013 to 2022.Unit: d/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |