1 引言
2 研究区域和数据方法
2.1 站点及观测资料介绍
2.2 生态系统呼吸Re模型的选择
表 1 2012 -2017年不同模型拟合效果和 Re 计算结果Table 1 Fitting effects and calculation results of different models of Re from 2012 to 2017 |
| R 2 | Re年累计结果/(gC·m-2·a-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 6年平均 | ||
| 指数模型 | 0.70 | 1000.0 | 940.5 | 750.7 | 694.7 | 963.3 | 892.1 | 873.6 |
| Arrhenius模型 | 0.70 | 989.1 | 933.3 | 744.6 | 688.4 | 988.8 | 904.5 | 874.8 |
| 连乘模型 | 0.70 | 1132.4 | 873.2 | 645.5 | 646.0 | 839.2 | 693.1 | 804.9 |
| 复合模型(本文) | 0.71 | 979.4 | 896.6 | 658.1 | 646.1 | 870.3 | 741.2 | 798.6 |
2.3 数据分析方法
3 结果与分析
3.1 环境因子的年变化特征
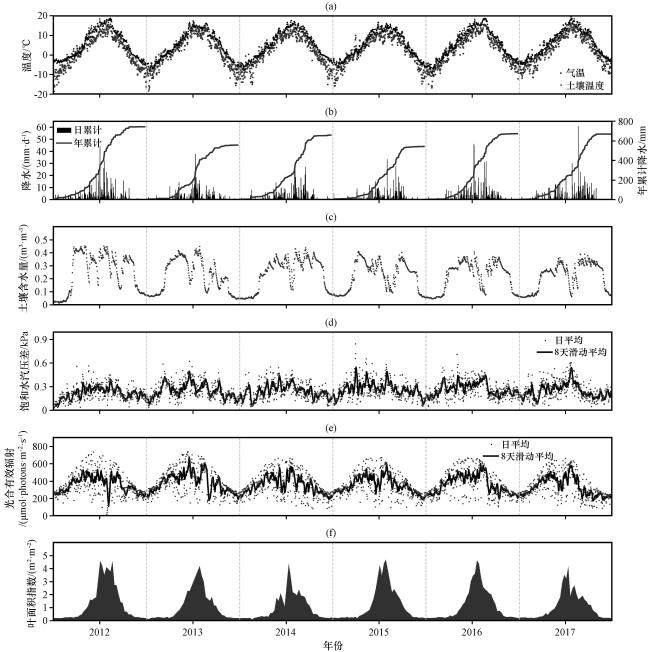
图1 2012 -2017年环境因子季节变化特征(a)气温(Ta)和土壤温度(Ts), (b)日降水(PRE)和年累计降水, (c)土壤含水量(SWC), (d)日平均及8天滑动平均饱和水汽压差(VPD), (e)日平均及8天滑动平均光合有效辐射(PAR), (f)叶面积指数(LAI) Fig.1 Seasonal variation characteristics of environmental factors in 2012 -2017, (a)air temperature (Ta) and soil temperature (Ts), (b)daily and cumulative precipitation (PRE), (c)soil water content (SWC), (d)vapor pressure deficit (VPD), (e)photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), (f) leaf area index (LAI) |
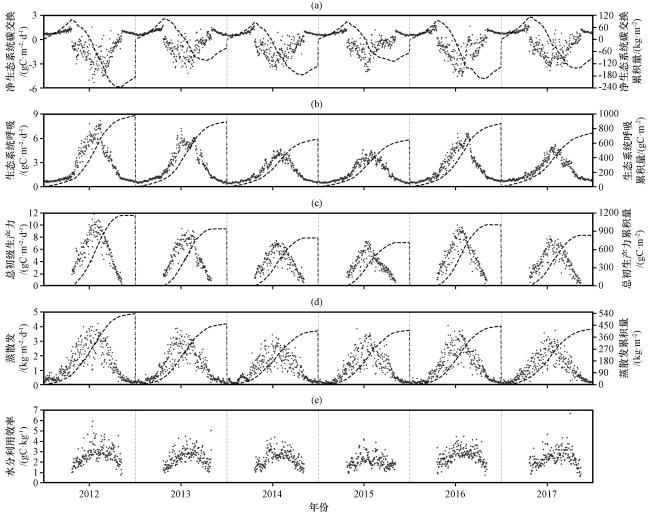
3.2 碳水通量的年变化特征
表2 青藏高原不同研究区域的 NEE 年平均值Table 2 The annual average NEE values of different research areas on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau |
| 观测地区 | 位置 | 海拔/m | 研究年份 | 下垫面类型 | NEE/(gC·m-2·a-1) | 文献来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玛曲 | 33.89°N, 102.14°E | 3434 | 2012 -2017 | 高寒草甸 | -109.69 | 本文 |
| 那曲 | 31.37°N, 91.90°E | 4509 | 2008 | 高寒草甸 | -41.30 | (朱志鹍等, 2015) |
| 当雄 | 30.50°N, 91.07°E | 4333 | 2009 -2011 | 高寒草甸 | 18.09±40.66 | (徐玲玲等, 2024) |
| 若尔盖 | 32.80°N, 102.60°E | 3500 | 2015 -2020 | 高寒草甸 | 94.69±86.44 | (Wang et al, 2022) |
| 海北 | 37.32°N, 101.32°E | 3220 | 2013 -2014 | 嵩草草甸 | -76.91 | (赵亮等, 2005) |
| 三江源 | 34.30°N, 100.50°E | 3980 | 2005 -2006 | 人工草地 | -49.35 | (赵亮等, 2008) |
| 海北 | 37.32°N, 101.32°E | 3220 | 2013 -2014 | 灌丛草甸 | -14.45 | (赵亮等, 2005) |
| 海北 | 37.32°N, 101.32°E | 3220 | 2013 -2014 | 沼泽草甸 | 130.36 | (赵亮等, 2005) |
| 大沙龙 | 38.84°N, 98.94°E | 3739 | 2014 -2018 | 沼泽草甸 | -284.12 | (Wang et al, 2021) |
| 玛曲 | 33.89°N, 102.14°E | 3533 | 2013 -2018 | 嵩草草甸 | -246.90 | (Wang et al, 2021) |
| 阿柔 | 38.03°N, 100.45°E | 3033 | 2013 -2018 | 嵩草草甸 | -218.69 | (Wang et al, 2021) |
| 那曲BJ | 31.37°N, 91.90°E | 4509 | 2013 -2014 | 嵩草草甸 | 1.51 | (Wang et al, 2021) |
| 纳木错 | 30.77°N, 90.98°E | 4730 | 2008 -2009 | 草甸草原 | 31.08 | (Wang et al, 2021) |
表3 青藏高原不同研究区域的 ET 年平均值Table 3 The annual average ET values of different research areas on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau |
| 观测地区 | 位置 | 海拔/m | 研究年份 | 下垫面类型 | ET/(kg·m-2·a-1) | 文献来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玛曲 | 33.89°N, 102.14°E | 3434 | 2012 -2017 | 高寒草甸 | 446.50 | 本文 |
| 果洛 | 34.35°N, 100.48°E | 3963 | 2007 | 高寒草甸 | 481.90 | (张立锋等, 2017) |
| 若尔盖 | 34.57°N, 102.72°E | 3231 | 2013 -2014 | 高寒草甸 | 673.60 | (郭小璇等, 2021) |
| 海北 | 37.65°N, 102.32°E | 3293 | 2003 -2011 | 高寒草甸 | 529.00 | (郑涵等, 2013) |
| 唐古拉 | 33.03°N, 92.00°E | 5170 | 2007 -2013 | 高寒草甸 | 247.00~321.00 | (王利辉等, 2019) |
| 阿柔 | 38.03°N, 100.45°E | 3033 | 2013 -2017 | 高寒草原 | 654.80 | (Zhang and Dou, 2020) |
表 4 不同研究区域的 WUE 年平均值Table 4 The annual average WUE values of different research areas |
| 研究地区 | 位置 | 数据资料 | 研究年份 | 下垫面类型 | WUE/(gC·kg-1) | 文献来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玛曲站点 | 33.89°N, 102.14°E | 观测 | 2012 -2017 | 高寒草甸 | 2.02 | 本文 |
| 海北站点 | 37.60°N, 101.33°E | 观测 | 2003 -2010 | 金露梅灌丛 | 0.40 | (王云英等, 2021) |
| 青藏高原 | 区域 | 遥感 | 2001 -2020 | 草原、 灌丛 | 1.17 | (崔茜琳等, 2022) |
| 中国草地 | 区域 | 模型 | 2000 -2015 | 草地 | 1.10 | (陈鑫涛和邓超, 2021) |
| 中国草甸 | 区域 | 观测 | 2003 -2005 | 高寒草甸 | 0.90 | (Hu et al, 2008) |
3.3 碳水通量生长季的日变化特征
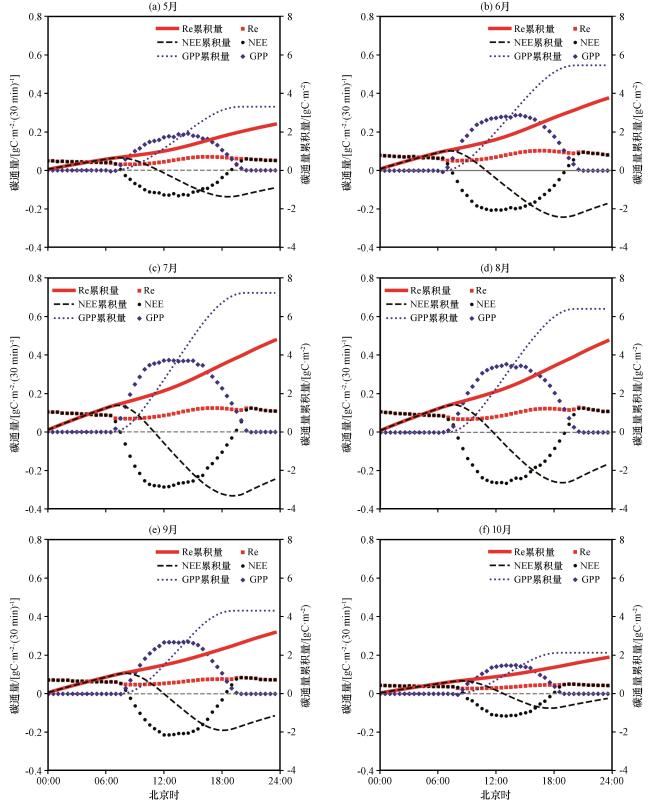
3.3.1 碳通量生长季日变化特征
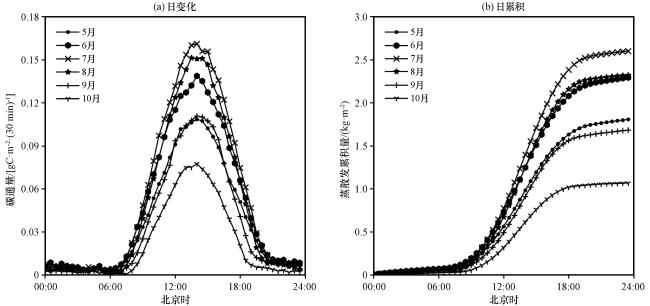
3.3.2 ET 生长季日变化特征
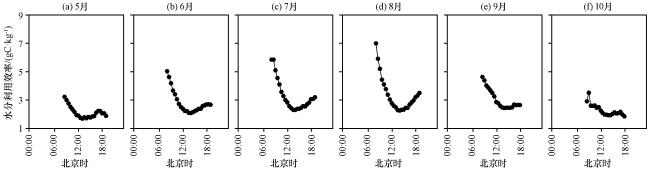
3.3.3 WUE 生长季日变化特征
3.4 碳水通量、 水分利用效率与环境因子之间的关系
表 5 2012 -2017年生长季 Re 对潜在驱动因素的多元逐步回归的偏相关系数Table 5 Partial correlation coefficients between Re and potential driving factors of multivariate stepwise regression during the growing season of 2012 -2017 |
| 逐步回归方程(Re) | R 2 | Ts | LAI | PAR | VPD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Re=-0.106+0.314Ts | 0.80 | 0.90 | |||
| Re=0.007+0.265Ts+0.225LAI | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.18 | ||
| Re=-0.139+0.261Ts+0.223LAI+0.000PAR | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.18 | 0.05 | |
| Re=-0.132+0.267Ts+0.213LAI+0.001PAR-0.698VPD | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
表 6 2012 -2017年生长季 ET 对潜在驱动因素的多元逐步回归的偏相关系数Table 6 Partial correlation coefficients between ET and potential driving factors of multivariate stepwise regression during the growing season of 2012 -2017 |
| 逐步回归方程(ET) | R 2 | PAR | Ts | SWC | LAI | VPD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET=0.33-0.00PAR | 0.52 | 0.72 | ||||
| ET=-0.52+0.00PAR+0.11Ts | 0.81 | 0.58 | 0.55 | |||
| ET=-1.07+0.00PAR+0.11Ts+1.50SWC | 0.83 | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.15 | ||
| ET=-0.94+0.00PAR+0.09Ts+1.32SWC+0.12 LAI | 0.84 | 0.60 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 0.17 | |
| ET=-0.99+0.00PAR+0.08Ts+1.43SWC+0.13LAI +0.67VPD | 0.84 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.09 |
表7 2012 -2017年生长季 WUE 对潜在驱动因素的多元逐步回归的偏相关系数Table 7 Partial correlation coefficients between WUE and potential driving factors of multivariate stepwise regression during the growing season of 2012 -2017 |
| 逐步回归方程(WUE) | R 2 | Ts | PAR | LAI | VPD | PRE | Ta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WUE =1.50+0.09Ts | 0.23 | 0.48 | |||||
| WUE =2.14+0.11Ts-0.00PAR | 0.40 | 0.59 | -0.43 | ||||
| WUE =2.23+0.07Ts-0.00PAR+0.17LAI | 0..42 | 0.38 | -0.43 | 0.26 | |||
| WUE =2.24+0.08Ts-0.00PAR+0.15LAI-1.24VPD | 0.43 | 0.44 | -0.31 | 0.23 | -0.18 | ||
| WUE =2.30+0.09Ts-0.00PAR+0.15LAI-1.48VPD-0.02PRE | 0.44 | 0.49 | -0.32 | 0.23 | -0.21 | -0.11 | |
| WUE =2.19+0.12Ts-0.00PAR+0.14LAI-1.16VPD-0.01PRE-0.03Ta | 0.45 | 0.65 | -0.34 | 0.22 | -0.17 | -0.10 | -0.18 |
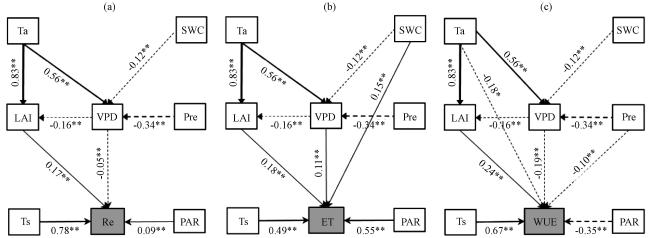
图6 2012 -2017年生长季日Re (a)、 ET (b)和WUE (c) 的结构方程模型实线和虚线表示正、 负效应, 数值表示标准路径系数, “**”表示p<0.01, “*”表示p<0.05 Fig.6 Structural equation models for daily Re (a), ET (b) and WUE (c) during the growing season in 2012 -2017.Solid and dotted lines represent positive and negative paths, and values are the standard path coefficient.“**” represent p<0.01 and “*” represent p<0.05 |