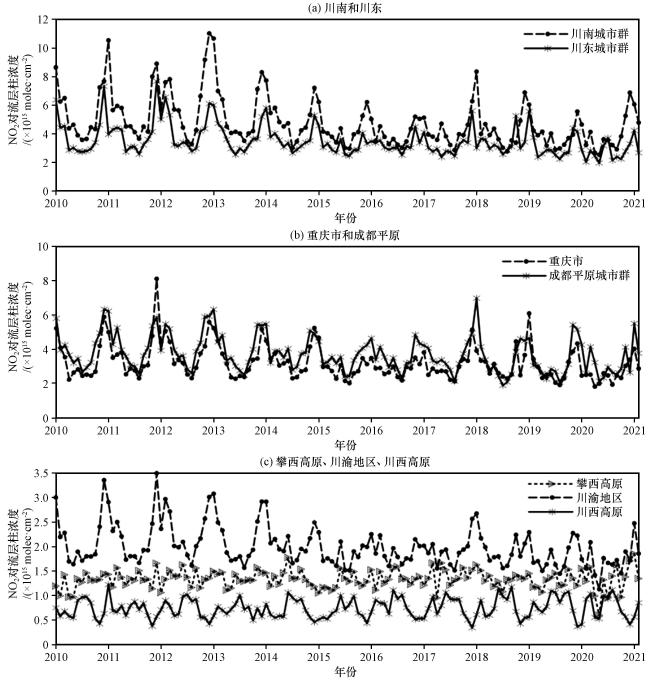
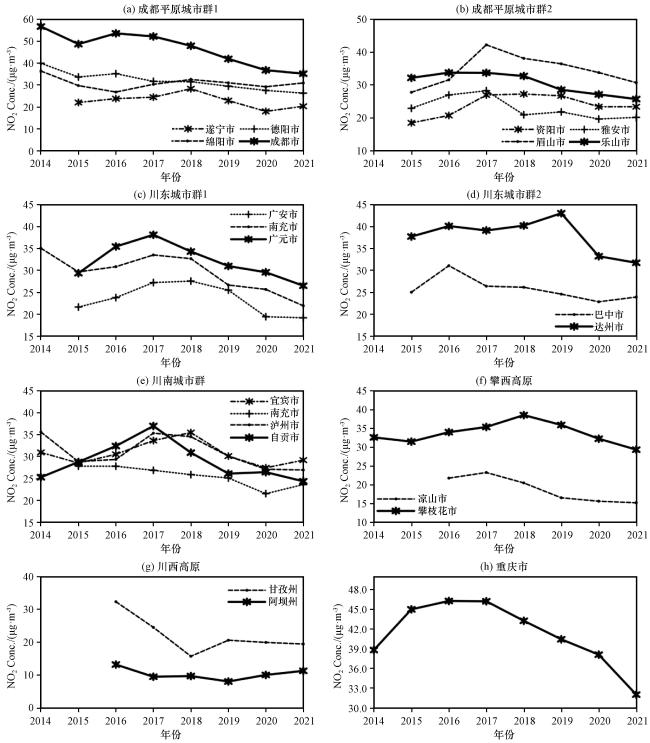
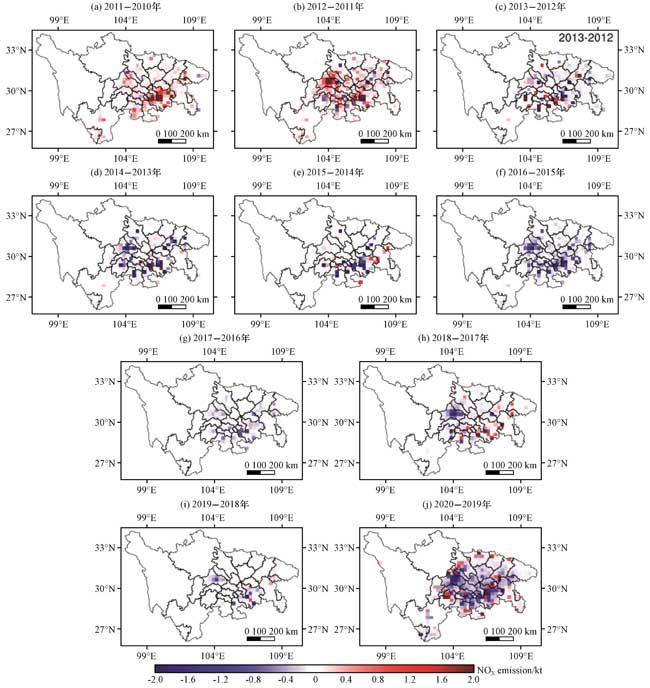
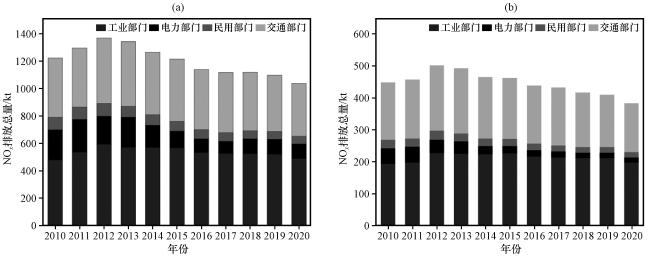
图9为2014 -2021年川渝地区各城市地面环境监测的NO
2年均浓度变化趋势。从
图9(a)~(b)可以看出, 成都市的NO
2浓度最高, 与之前的分析一致。相比2014年, 2015年成都、 绵阳和德阳市的NO
2年均浓度有所下降。2016年, 大多数城市的NO
2年均浓度较2015年有所上升, 其中雅安市增幅最大, 达到17.9%。成都市2016年NO
2年均浓度为53.7 μg·m
-3, 比第二位的绵阳市高出18 μg·m
-3。2017年, 资阳市和眉山市的NO
2年均浓度增幅显著, 分别上升33.86%和30.43%。之后, 大多数城市的NO
2年均浓度呈现下降趋势。到2021年, 成都市的NO
2年均浓度达到谷值, 较2014年下降了37.85%。总体来看, 成都平原的NO
2年均浓度在2015年下降到一个谷值后, 2016年和2017年有所回升, 2017年后保持缓慢下降。与OMI NO
2柱浓度的长期变化趋势相比, 地面观测的NO
2浓度和卫星观测的NO
2柱浓度变化趋势一致性较好。从
图9(e)中可以看出, 2015年泸州和宜宾的NO
2年均浓度有所下降, 而自贡市的NO
2年均浓度有所上升。2015 - 2021年, 除内江市的NO
2年均浓度保持稳定外, 其余三个城市的变化趋势与成都平原一致, 呈现先上升后下降的趋势。川东[
图9(c)~(d)]、 重庆[
图9 (h)]和攀西高原[
图9(f)]的城市也表现出相似的变化趋势, 但峰值出现的时间有所不同。大部分城市在2016年或2017年达到峰值, 之后缓慢下降。
图9(g)显示, 2016 -2021年阿坝州和甘孜州的NO
2浓度总体呈先下降后上升的趋势。甘孜州在2018年NO
2浓度达到谷值, 较2016年下降51.4%, 之后浓度有所上升, 但增幅不大。