1 引言
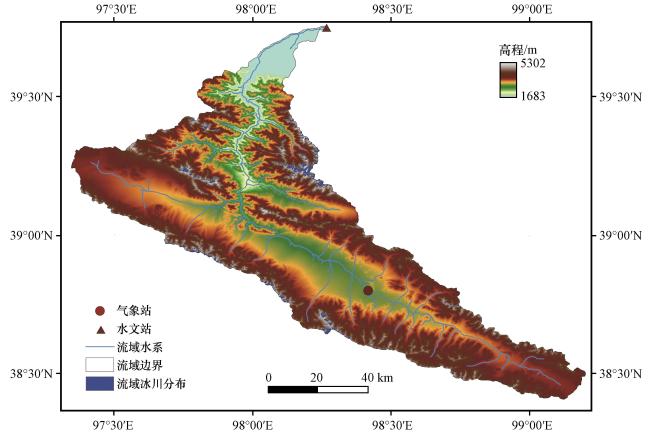
2 研究区概况
3 数据来源与模型构建
3.1 数据来源
3.2 HBV-light模型
表1 HBV-light模型参数及其范围Table 1 Introduction and range of HBV-light model parameters |
| 参数 | 说明 | 单位 | 参数值范围 | 率定结果 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冰川积雪消融模块 | TT | 区分降雨、 降雪的临界温度 | ℃ | –3~3 | –0.79 |
| SFCF | 降雪的校正系数 | 0~0.9 | 0.36 | ||
| CFMAX | 积雪度日因子 | mm·(℃·d)-1 | 1.5~5 | 2 | |
| CFGlacier | 冰川度日因子校正系数 | 1.2~2 | 1.32 | ||
| CFSlope | 坡向朝南比朝北的冰川消融增加量 | 1~3 | 2.40 | ||
| CFR | 重冻结系数 | 0.02~0.1 | 0.02 | ||
| CWH | 持水量 | 0.1~0.4 | 0.11 | ||
| 土壤模块 | FC | 土壤田间持水量 | mm | 100~550 | 265.55 |
| LP | 土壤含水量/田间持水量临界值 | 0.3~1 | 0.87 | ||
| BETA | 产流有关的经验参数 | 1~5 | 2.46 | ||
| 响应模块 | PERC | 土壤上层水库到下层水库的最大渗透率 | mm·d-1 | 0~4 | 0.81 |
| UZL | 上层水库含水量的阈值 | mm | 0~70 | 58.72 | |
| K0 | 洪峰的出流系数 | d-1 | 0.1~0.5 | 0.29 | |
| K1 | 壤中流的出流系数 | d-1 | 0.01~0.2 | 0.09 | |
| K2 | 基流的出流系数 | d-1 | 0.00005~0.1 | 0.003 | |
| 汇流模块 | MAXBAS | 河道汇流参数 | d | 1~2.5 | 2.43 |
3.3 模型评价指标
4 结果与分析
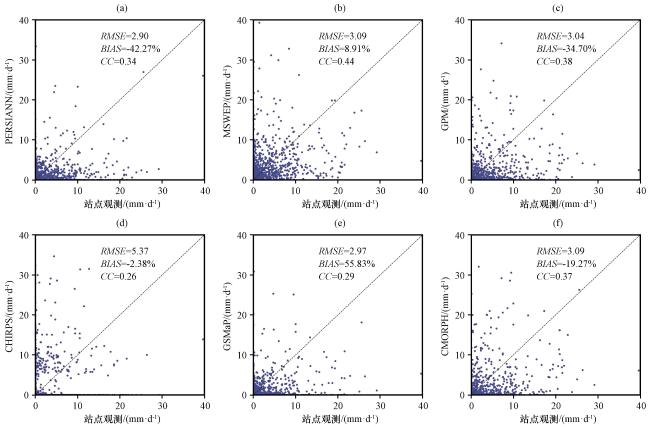
4.1 多源遥感降水在讨赖河流域的水文适用性评估
图2 不同降水产品与站点观测降水的散点分布 (a)PERSIANN, (b)MSWEP, (c)GPM, (d)CHIRPS, (e)GSMaP, (f)CMORPHFig.2 Scatterplots of the daily precipitation between different precipitation products and in-situ observations.(a) PERSIANN, (b) MSWEP, (c) GPM, (d) CHIRPS, (e) GSMaP, (f) CMORPH |
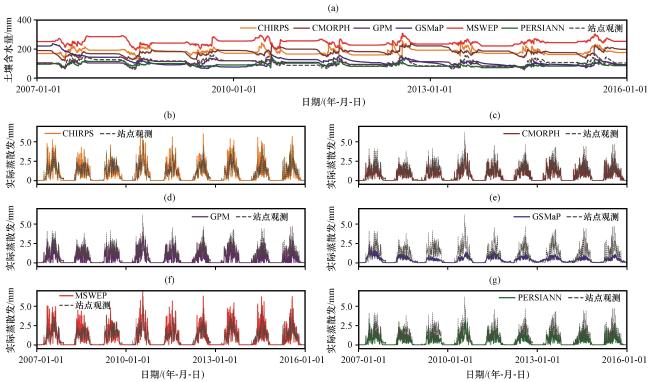
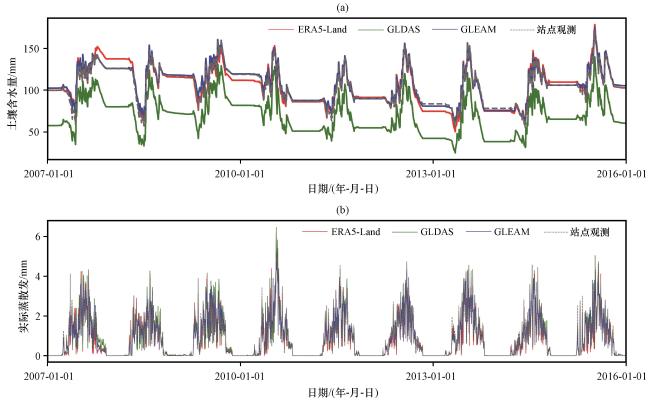
图4 不同降水产品驱动下水文模拟得到的土壤含水量(a)和实际蒸散发(b~g)(b)CHIRPS, (c)CMORPH, (d)GPM, (e)GSMaP, (f)MSWEP, (g)PERSIANNFig.4 Time series of soil water content (a) and actual evapotranspiration (b~g) from hydrologic simulations driven by different precipitation products.(b) CHIRPS, (c) CMORPH, (d) GPM, (e) GSMaP, (f) MSWEP, (g) PERSIANN |
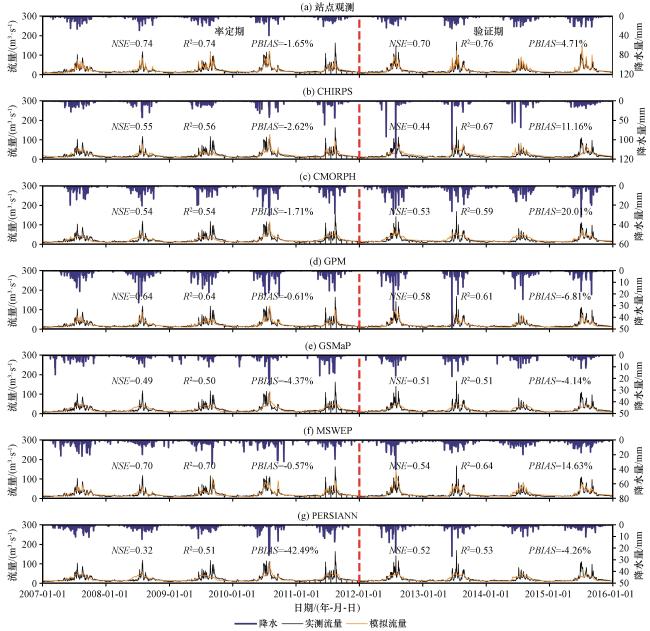
表2 2007 -2015年不同网格产品驱动径流模拟在讨赖河流域的水量平衡分析Table 2 Water balance analysis of streamflow simulations driven by different gridded products in the Taolai river basin from 2007 to 2015 |
| 网格产品 | 水量平衡指标/(mm·a-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降水量 | 模拟径流深 | 实测径流深 | 实际蒸散发 | 潜在蒸散发 | 土壤含水量 | 水量平衡方程闭合差 | |
| CHIRPS | 377.56 | 90.79 | 87.85 | 294.57 | 880.88 | 180.30 | -7.81 |
| CMORPH | 323.07 | 94.61 | 87.85 | 231.70 | 863.31 | 180.39 | -3.25 |
| 站点观测数据 | 392.43 | 88.82 | 87.85 | 294.68 | 856.85 | 104.77 | 8.94 |
| GPM | 254.50 | 84.95 | 87.85 | 189.22 | 915.56 | 100.68 | -19.68 |
| GSMaP | 164.54 | 84.10 | 87.85 | 137.34 | 798.69 | 111.35 | -56.90 |
| MSWEP | 421.22 | 93.14 | 87.85 | 310.20 | 882.84 | 246.22 | 17.89 |
| PERSIANN | 225.34 | 86.39 | 87.85 | 167.99 | 871.32 | 90.18 | -29.03 |
| ERA5-Land | 392.43 | 88.93 | 87.85 | 291.37 | 750.76 | 105.44 | 12.13 |
| GLDAS | 392.43 | 84.89 | 87.85 | 310.56 | 1633.29 | 68.83 | -3.02 |
| GLEAM | 392.43 | 87.65 | 87.85 | 294.29 | 587.44 | 106.42 | 10.49 |
| MOD11A1 | 392.43 | 88.40 | 87.85 | 306.58 | 843.58 | 79.04 | -2.55 |
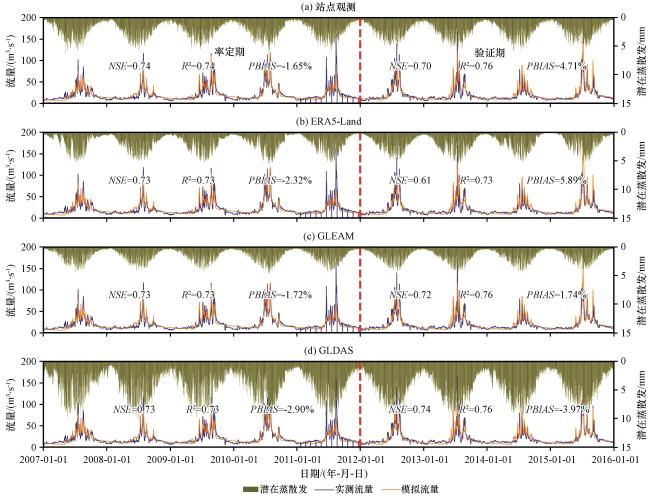
4.2 潜在蒸散发产品在讨赖河流域的水文适用性评估
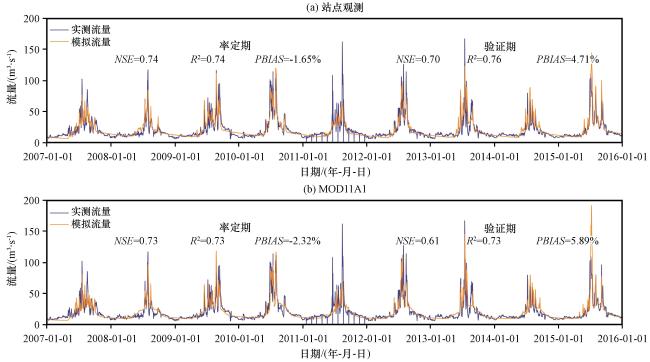
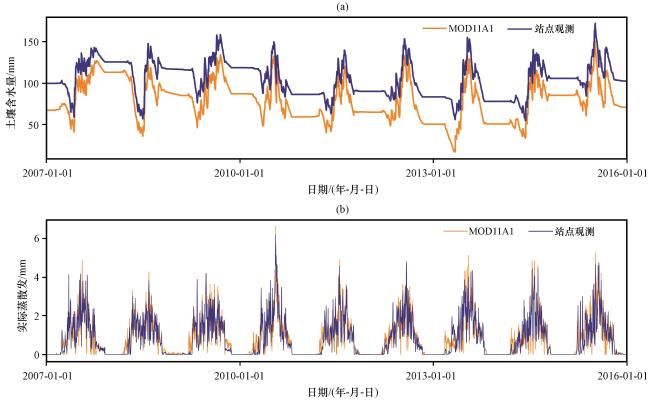
4.3 地表温度产品在讨赖河流域的水文适用性评估
图7 MOD11A1作为HBV-light输入在讨赖河的径流模拟效果 (a)站点观测, (b)MOD11A1Fig.7 Streamflow simulations driven by MOD11A1 product in the Taolai river basin.(a) observation, (b) MOD11A1 |