 PDF(12553 KB)
PDF(12553 KB)


云南不同类型大风时空特征分析
马文倩, 李华宏, 陈小华, 闵颖, 李耀孙, 何钰
 PDF(12553 KB)
PDF(12553 KB)
云南不同类型大风时空特征分析
Analysis on the Spatio-temporal Characteristics for Different Types of Strong Winds over Yunnan
基于多种观测资料, 将2013 -2021年云南125个国家站17 m·s-1及以上16778个大风划分为热低压大风、 雷暴大风、 局地大风、 冷空气大风、 南支槽前大风、 500 hPa偏西急流背景下偏西大风、 台风大风和高原槽后大风8种类型, 对除局地大风外的7种类型大风时空分布及风向风速特征进行了分析。云南大风主要为热低压大风, 其次为雷暴大风, 大风主要发生在云南西北部、 中部和东部; 除雷暴大风外, 其余类型大风风向可大致根据大风成因判定, 大风风速多为7~9级, 10级及以上风速分布不连续性强, 雷暴大风和南支槽前大风发生站次相对热低压大风少, 但其造成极端大风的可能性更高; 发生站次年变化方面, 大风主要发生在冬春季节, 3月最多, 雷暴大风年变化呈现出双峰结构, 除4月主高峰外, 8月还有一个次高峰, 同时雷暴大风发生日数年变化也呈现双峰结构, 8月次高峰大风日数与最高峰4月相当, 即春季雷暴大风组织性较强, 夏季雷暴大风则呈现出零散的特征; 发生站次日变化方面, 热低压大风主要发生在白天, 15:00 -15:59(北京时, 下同)最多, 雷暴大风和南支槽前大风主要发生在午后, 16:00 -17:59最多, 冷空气大风主要发生在午后至凌晨, 18:00 -19:59最多, 500 hPa偏西急流背景下偏西大风有两个主要发生时间段, 午后和凌晨, 午后发生站次相对较多, 台风大风主要发生在白天, 16:00 -17:59较多, 高原槽后大风主要发生在白天和刚入夜时, 15:00 -16:59相对较多。
Based on multiple observations, 16778 strong winds with speed equal to or greater than 17 m·s-1 from 125 national meteorological stations over Yunnan from 2013 to 2021 are divided into 8 types: thermal low winds, thunderstorm winds, local winds, cold-air winds, winds before southern trough, winds under 500 hPa westerly jet, typhoon winds and winds after plateau trough.The characteristics of spatio-temporal distribution and wind direction/speed of all types of winds except for the local winds are explored.The most frequent strong winds over Yunnan are thermal low winds, followed by thunderstorm winds.The strong winds are mainly observed over the northwest, central, and eastern parts of Yunnan.Except for thunderstorm winds, the wind directions of strong winds could be determined by the causes of their occurrence.The wind speeds mainly range from level 7 to level 9, and the distribution of wind speeds which are equal to or greater than level 10 shows strong discontinuity.Even though the frequencies of thunderstorm winds and winds before southern trough are less than that of thermal low winds, the two types of winds have a higher ability to cause extremely strong winds.The annual variation of occurring times shows that the winds mainly occur in winter and spring, with the most frequency in March.The annual variation of occurring times of thunderstorm winds shows a bimodal structure with a main peak in April and a sub peak in August.Meanwhile, the annual variation of occurring days of thunderstorm winds also shows a bimodal structure, the occurring days of the sub peak in August are comparable to that of the main peak in April, indicating that thunderstorm winds occurring in spring are relatively organized, while thunderstorm winds occurring in summer are relatively scattered.For the diurnal variation of occurring times, the thermal low winds mainly occur in daytime, with the highest occurring frequency at 15:00 to 15:59 (Beijing time, the same below).The thunderstorm winds and winds before southern trough mainly occur in afternoon, with the highest occurring frequency at 16:00 to 17:59.The cold-air winds mainly occur from the afternoon to the early morning, with the highest occurring frequency at 18:00 to 19:59.The winds under 500 hPa westerly jet have two periods with high frequencies, afternoon and early morning, and more winds occur in the afternoon.The typhoon winds mainly occur in daytime, with the highest frequency occurring at 16:00 to 17:59.The winds after plateau trough mainly occur in daytime and the beginning of the night, and more winds occur at 15:00 to 16:59.
大风 / 云南 / 分型 / 时空特征 {{custom_keyword}} /
strong winds / Yunnan / classification / spatio-temporal characteristics {{custom_keyword}} /
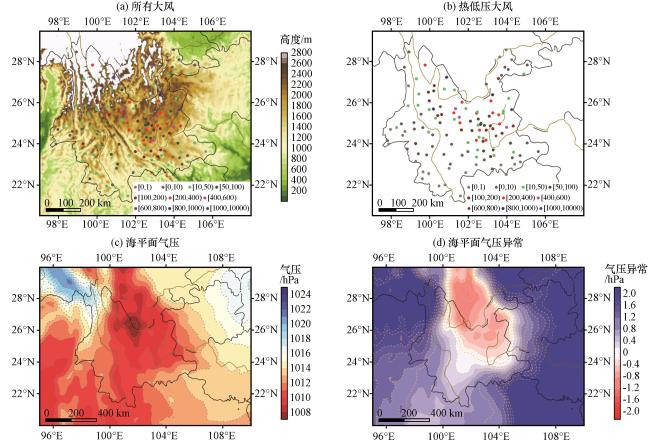
图2 云南125个国家站2013 -2021年发生大风次数(彩色圆点, 单位: 次数)叠加地形(填色, 单位: m)(a)、 发生热低压大风次数(b, 单位: 次数)、 2013 -2021年2 -4月15:00海平面气压平均值(等值线和彩色区, c, 单位: hPa)和相对整个研究时段15:00海平面气压异常值(等值线和彩色区, d, 单位: hPa)Fig.2 The occurring times of all strong winds (colored dots, unit: times) and topography (shading, unit: m) (a), the occurring times of thermal low winds (b, unit: times) at 125 national stations in Yunnan from 2013 to 2021, the composite mean (contour line and coloral area, c, unit: hPa) and anomaly (contour line and coloral area, d, unit: hPa) of sea level pressure at 15:00 during February to April from 2013 to 2021 |
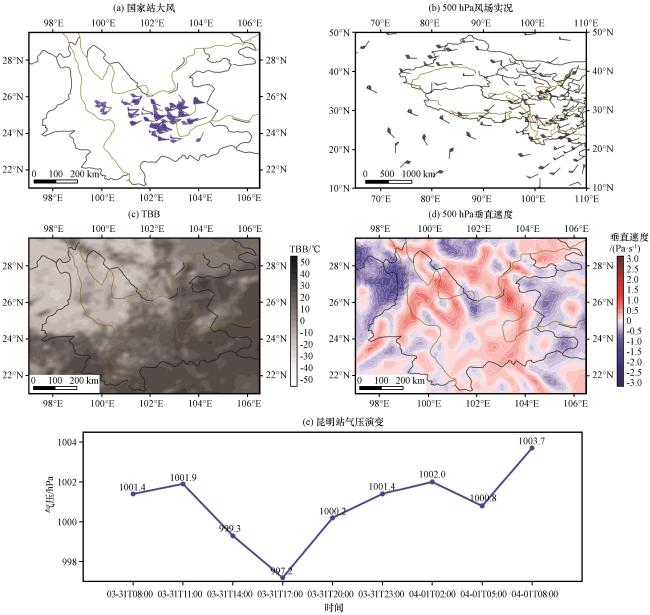
图3 2021年3月31日08:00 -19:59云南国家站17 m·s-1及以上大风(a, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 08:00 500 hPa风场(b, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 15:00 FY-2H-TBB(c, 单位: ℃)、 15:00 500 hPa垂直速度(d, 单位: Pa·s-1)及2021年3月31日08:00至4月1日08:00逐3 h昆明站地面气压演变(e, 单位: hPa)Fig.3 The winds with speed equal to or greater than 17 m·s-1 occurring from 08:00 to 19:59 on March 31, 2021 at national stations in Yunnan (a, wind barbs, unit: m·s-1), the winds on 500 hPa at 08:00 (b, wind barbs, unit: m·s-1), the FY-2H TBB at 15:00 (c, unit: °C), the vertical velocity on 500 hPa at 15:00 (d, unit: Pa·s-1), and the evolution of surface pressure at Kunming every 3 hours from 08:00 on March 31 to 08:00 on April 1, 2021 (e, unit: hPa) |
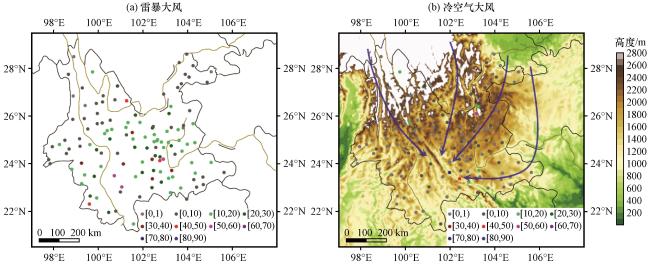
图4 云南125个国家站2013 -2021年发生雷暴大风次数(a, 单位: 次数)和冷空气大风次数(彩色圆点, 单位: 次数)叠加地形(填色, 单位: m)以及进入云南的冷空气常见路径(蓝线箭头)(b)Fig.4 The occurring times of thunderstorm winds (a, unit: times) and cold-air winds (colored dots, unit: times) overlaying the topography (shading, unit: m) and the main pathways of cold air entering Yunnan (blue line arrows) (b) at 125 national stations in Yunnan from 2013 to 2021 |
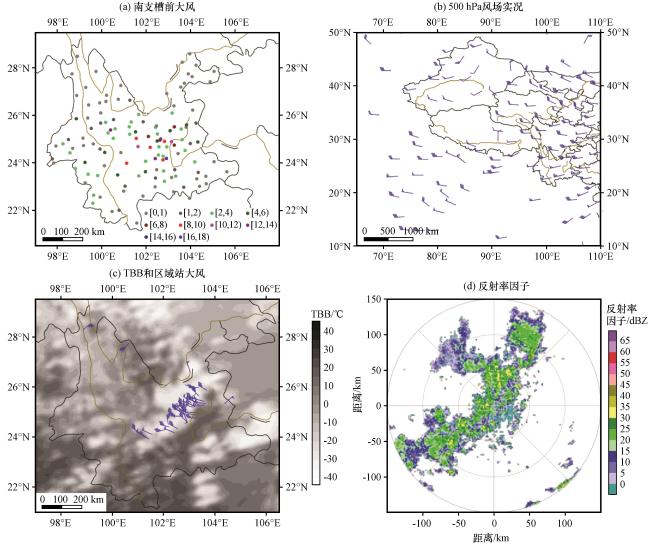
图5 云南125个国家站2013 -2021年发生南支槽前大风次数(a, 单位: 次数)、 2020年3月3日08:00 500 hPa风场(b, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 2020年3月3日17:00 -17:59区域站17 m·s-1及以上大风(风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加17:00 FY-2H-TBB(填色, 单位: ℃)(c)和2020年3月3日17:03昆明雷达0.5°仰角反射率因子(d, 单位: dBZ)Fig.5 The occurring times of winds before southern trough at 125 national stations in Yunnan from 2013 to 2021 (a, unit: times), the winds on 500 hPa at 08:00 on March 3, 2020 (b, wind barbs, unit: m·s-1), the winds with speed equal to or greater than 17 m·s-1 occurring from 17:00 to 17:59 on March 3, 2020 at regional stations (wind barbs, unit: m·s-1) and FY-2H TBB (shading, unit: °C) at 17:00 on March 3, 2020 (c), the reflectivity factor of 0.5 elevation of Kunming radar at 17:03 on March 3, 2020 (d, unit: dBZ) |
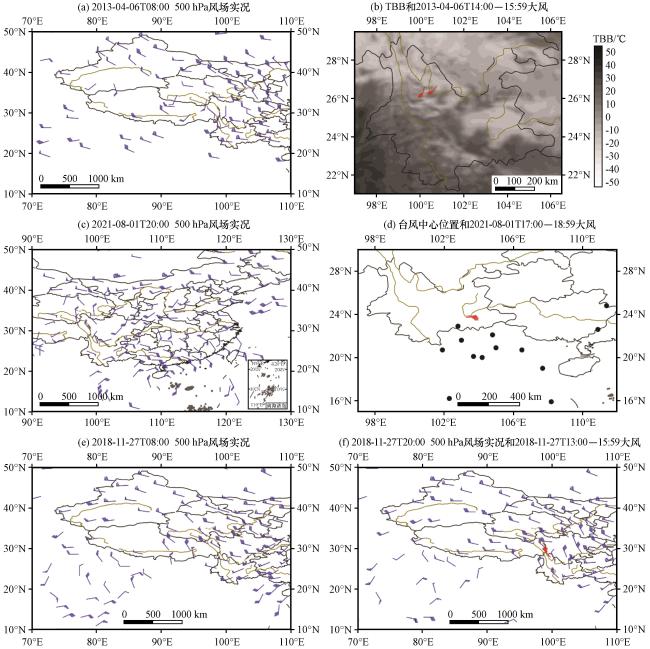
图6 2013年4月6日08:00 500 hPa风场实况(a, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 2013年4月6日14:00 -15:59国家站大风(风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加2013年4月6日14:30 FY-2F-TBB(填色, 单位: ℃)(b)、 2021年8月1日20:00 500 hPa风场实况(c, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 2021年8月1日17:00 -18:59国家站大风(风羽, 单位: m·s-1)及所有台风大风发生时台风中心位置(黑色圆点, d)、 2018年11月27日08:00 (e)和20:00 (f) 500 hPa风场实况(风羽, 单位: m·s-1), 20:00实况叠加13:00 -15:59国家站大风(f, 红色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)Fig.6 The winds on 500 hPa at 08:00 on April 6, 2013 (a, wind barbs, unit: m·s-1), the winds with speed equal to or greater than 17 m·s-1 occurring from 14:00 to 15:59 on April 6, 2013 at national stations (wind barbs, unit: m·s-1) and FY-2F TBB (shading, unit: °C) at 14:30 on April 6, 2013 (b), the winds on 500 hPa at 20:00 on August 1, 2021 (c, wind barbs, unit: m·s-1), the winds with speed equal to or greater than 17 m·s-1 occurring from 17:00 to 18:59 on August 1, 2021 at national stations (wind barbs, unit: m·s-1)and the centers of typhoons (black dots) when all typhoon winds occur (d), the winds on 500 hPa at 08:00 (e, wind barbs, unit: m·s-1) and 20:00 (f, wind barbs, unit: m·s-1) overlaying the winds with speed equal to or greater than 17 m·s-1 occurring from 13:00 to 15:59 at national stations (f, red wind barbs, unit: m·s-1) on November 27, 2018 |
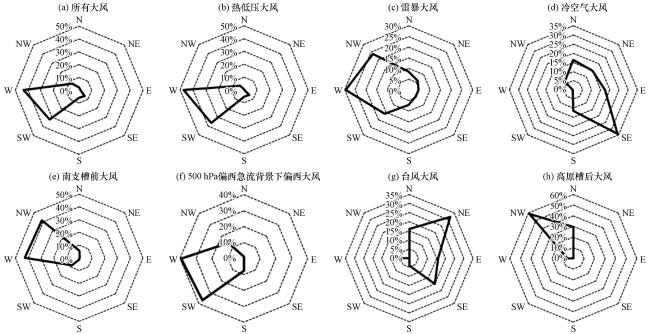
图7 所有大风和不同类型大风风向玫瑰图Fig.7 The rose charts of wind directions for all and different types of strong winds |
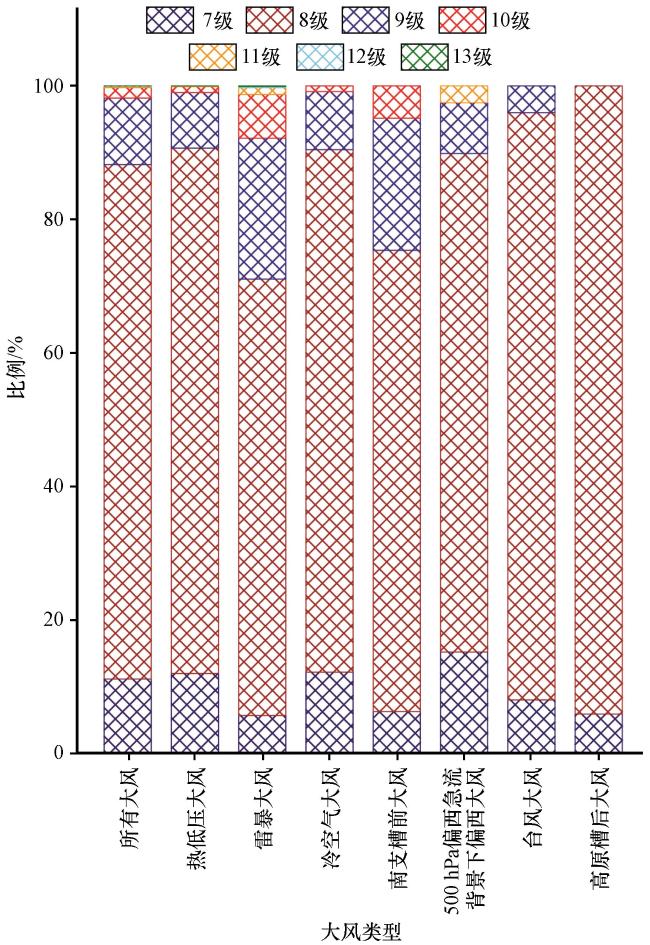
图8 所有大风和不同类型大风不同等级大风发生比例(单位: %)7级风统计的风速区间为[171] m·s-1, 8级为[17.2, 207] m·s-1、 9级为[20.8, 244] m·s-1、 10级为[24.5, 284] m·s-1、 11级为[28.5, 32.6] m·s-1、 12级为[32.7, 36.9] m·s-1、 13级为[37.0, 414] m·s-1 Fig.8 The proportions of winds with different levels for all and different types of strong winds.Unit: %.The wind speed range for level 7 is [171] m·s-1, level 8 is [17.2, 207] m·s-1, level 9 is [20.8, 244] m·s-1, level 10 is [24.5, 284] m·s-1, level 11 is [28.5, 32.6] m·s-1, level 12 is [32.7, 36.9] m·s-1, and level 13 is [37.0, 414] m·s-1 |
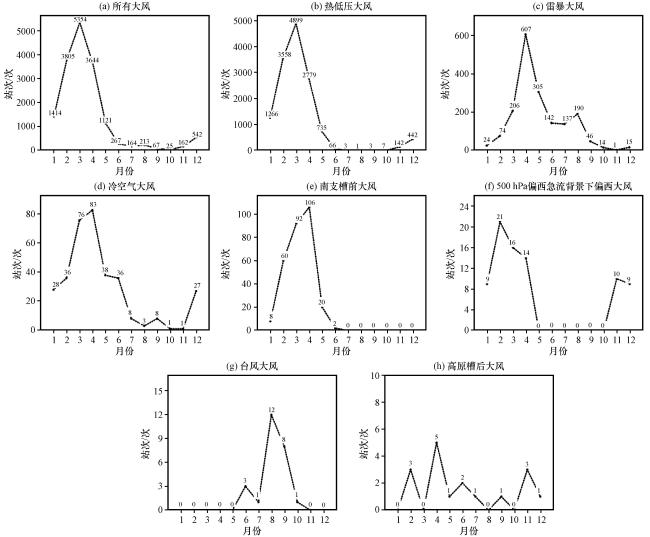
图9 所有大风和不同类型大风发生站次年变化Fig.9 The annual variations of occurring times for all and different types of strong winds |
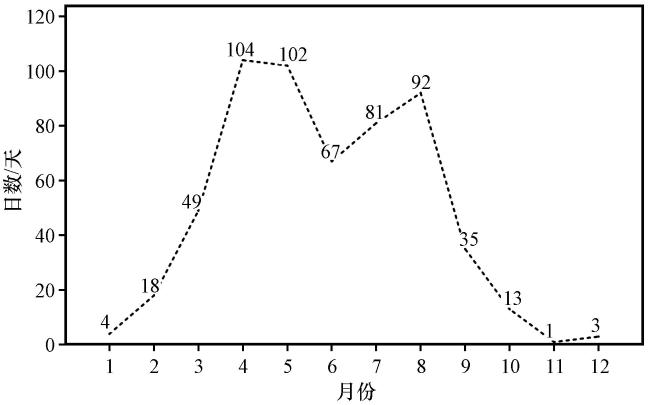
图10 雷暴大风日数年变化Fig.10 The annual variation of occurring days for thunderstorm winds |
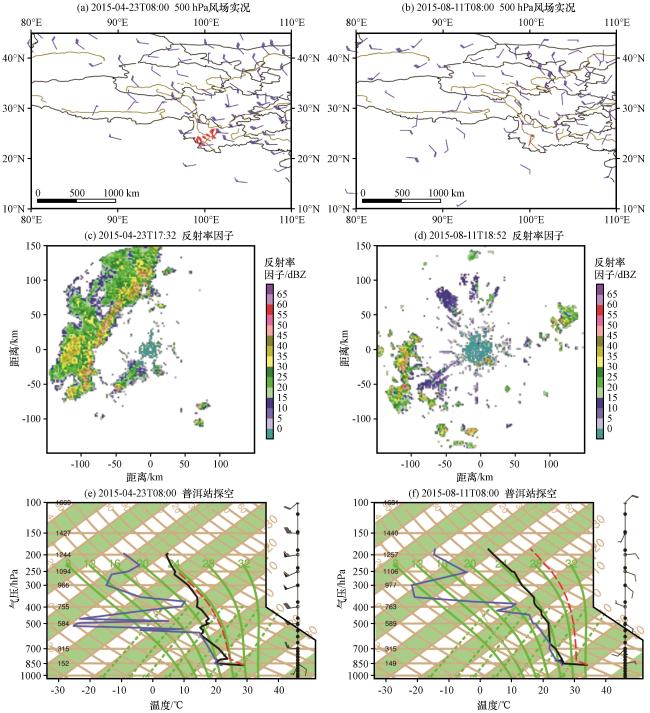
图11 2015年4月23日08:00 500 hPa风场实况(蓝色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加17:00 -17:59普洱区域站7级及以上大风(风速≥13.9 m·s-1, 红色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)(a)、 2015年8月11日08:00 500 hPa风场实况(蓝色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加18:00 -18:59普洱区域站7级及以上大风(红色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)(b)、 2015年4月23日17:32普洱0.5°仰角反射率因子(c, 单位: dBZ)、 2015年8月11日18:52普洱0.5°仰角反射率因子(d, 单位: dBZ)、 2015年4月23日08:00普洱订正探空(e)及2015年8月11日08:00普洱订正探空(f)Fig.11 The winds on 500 hPa at 08:00 on April 23, 2015 (blue wind barbs, unit: m·s-1) and the winds with speed equal to or greater than 13.9 m·s-1 occurring from 17:00 to 17:59 on April 23, 2015 at regional stations over Pu’er (red wind barbs, unit: m·s-1) (a), the winds on 500 hPa at 08:00 on August 11, 2015 (blue wind barbs, unit: m·s-1) and the winds with speed equal to or greater than 13.9 m·s-1 occurring from 18:00 to 18:59 on August 11, 2015 at regional stations over Pu’er (red wind barbs, unit: m·s-1) (b), the reflectivity factor of 0.5 elevation of Pu’er radar at 17:32 on April 23, 2015 (c, unit: dBZ), the reflectivity factor of 0.5 elevation of Pu’er radar at 18:52 on August 11, 2015 (d, unit: dBZ), the revised T-logP of Pu'er at 08:00 on April 23, 2015 (e) and the revised T-logP of Pu'er at 08:00 on August 11, 2015 (f) |
表1 所有大风和不同类型大风风速平均值、 25%和75%分位值、 最大值Table 1 The average, 25% and 75% percentile, maximum of wind speeds for all and different types of strong winds |
| 所有 大风 | 热低压 大风 | 雷暴 大风 | 冷空气 大风 | 南支槽前大风 | 500 hPa偏西急流背景下偏西大风 | 台风 大风 | 高原槽后大风 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值/(m·s-1) | 18.7 | 18.6 | 19.9 | 18.4 | 19.5 | 18.8 | 18.1 | 18.5 |
| 25%值/(m·s-1) | 17.4 | 17.4 | 17.8 | 17.3 | 17.9 | 17.3 | 17.4 | 17.4 |
| 75%值/(m·s-1) | 19.4 | 19.2 | 21.1 | 18.8 | 20.7 | 19.2 | 18.6 | 18.9 |
| 最大值/(m·s-1) | 39.4 | 39.4 | 38.1 | 26.3 | 26.6 | 31.1 | 20.9 | 20.7 |
表2 所有大风和不同类型大风发生站次时间变化特征Table 2 The temporal characteristics of occurring times for all and different types of strong winds |
| 所有 大风 | 热低压大风 | 雷暴 大风 | 冷空气 大风 | 南支槽前大风 | 500 hPa偏西急流背景下偏西大风 | 台风 大风 | 高原槽后大风 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年 变 化 | 主要时段 | 冬春季 | 冬春季 | 春夏季 | 冬春季、 初夏 | 2 -4月 | 11月至次年4月 | 夏秋季 | 全年 |
| 峰值月份 | 3月 | 3月 | 4月和8月/次高峰 | 3 -4月 | 4月 | 2月 | 8 -9月 | - | |
| 日 变 化 | 主要时段 | 白天 | 白天 | 午后 | 午后至凌晨 | 午后 | 午后和凌晨 | 白天 | 白天和刚入夜 |
| 峰值时间 | 15:00 -15:59 | 15:00 -15:59 | 16:00 -17:59 | 18:00 -19:59 | 16:00 -17:59 | 16:00 -16:59 | 16: 00 -17:59 | 15: 00 -16:59 | |
| -代表无数据(- represents no data available) |
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
白爱娟, 张永红, 吴佳浩, 等, 2021.华山景区大风变化特征及偏南大风的天气学研究[J].高原气象, 40(5): 1154-1163.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2020.00101.Bai A J ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
白虎志, 李栋梁, 董安祥, 等, 2005.青藏铁路沿线的大风特征及风压研究[J].冰川冻土, 27(1): 111-116.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2005.0017.Bai H Z ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
鲍艳松, 季凌潇, 李欢, 等, 2024.面向空投的青藏高原风场大涡模拟研究[J].高原气象, 43(2): 293-302.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2023.00051.Bao Y S ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
费海燕, 王秀明, 周小刚, 等, 2016.中国强雷暴大风的气候特征和环境参数分析[J].气象, 42(12): 1513-1521.DOI: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2016.12.009.Fei H Y ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
付桂琴, 曹欣, 2012.雷雨大风与河北电网灾害特征分析[J].气象, 38(3): 353-357.DOI: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2012.03.014.Fu G Q ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
胡娟, 李华宏, 李湘, 等, 2015.云南对流性大风天气的潜势预报及雷达回波特征[J].气象科技, 43(6): 1074-1084.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
孔锋, 李颖, 王一飞, 等, 2017.1961—2016年中国近地表大风日数时空分异特征研究[J].安徽农业科学, 45(31): 188-196.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
李晨轩, 韦志刚, 2024.1979-2021年中国南海海表风速和大风事件的变化特征[J].高原气象, 43(3): 696-710.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2023.00079.Li C X ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
李耀辉, 张存杰, 高学杰, 2004.西北地区大风日数的时空分布特征[J].中国沙漠, 24(6): 713-725.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
史培军, 张钢锋, 孔锋, 等, 2015.中国1961—2012年风速变化区划[J].气候变化研究进展, 11(6): 387-394.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1719.2015.06.002.Shi P J ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
孙继松, 戴建华, 何立富, 等, 2014.强对流天气预报的基本原理与技术方法——中国强对流天气预报手册[M].北京: 气象出版社, 13-83.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
王捷儒, 姚锦烽, 朴哲勇, 等, 2022.吉林西部风能太阳能资源互补特性研究[J].高原气象, 41(4): 1086-1095.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2022.00008.Wang J R ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
邢丽珠, 张方敏, 黄进, 等, 2021.1961-2018年内蒙古6级及以上大风日数时空变化特征[J].干旱区地理, 44(5): 1290-1298.DOI: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2021.05.10.Xing L Z ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
许美玲, 段旭, 杞明辉, 等, 2011.云南省天气预报员手册[M].北京: 气象出版社, 179.Xu M L, Duan X, Qi M H, et al, 2011.The manual for the weather forecasters for Yunnan province[M].Beijing: Meteorological Press, 179.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
薛桁, 朱瑞兆, 杨振斌, 等, 2001.中国风能资源贮量估算[J].太阳能学报, 22(2): 167-170.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
杨芳园, 杨素雨, 周稀, 等, 2018.昆明“2016.4.19”雷暴大风天气过程的中尺度特征分析[J].云南大学学报(自然科学版), 40(4): 716-725.DOI: 10.7540/j.ynu.20170556.Yang F Y ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
杨显玉, 朱俊橙, 文军, 等, 2023.南疆大风气候特征分析及其对沙尘天气的影响[J].高原气象, 42(1): 186-196.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2021.00043.Yang X Y ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
张俊兰, 杨霞, 魏娟娟, 等, 2020.玛依塔斯风区东风型风吹雪的天气学分型研究[J].高原气象, 39(5): 1023-1032.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2019.00105.Zhang J L ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
张太西, 王慧, 余行杰, 2021.新疆风灾时空分布特征分析[J].干旱区地理, 44(5): 1281-1289.DOI: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2021.05.09.Zhang T X ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
张晓龙, 沈冰, 黄领梅, 2020.基于ITPCAS再分析资料中国近地面风速时空变化特征[J].干旱区研究, 37(1): 1-9.DOI: 10.13866/j.azr.2020.01.01.Zhang X L ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
张云瑾, 戴卫帮, 程建刚, 2007.云南省“倒春寒”灾害性天气的研究[J].云南地理环境研究, 19(3): 15-17+25.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
张占峰, 张焕平, 马小萍, 2014.柴达木盆地平均风速与大风日数的变化特征[J].干旱区资源与环境, 28(10): 90-94.DOI: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2014.10.015.Zhang Z F ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿绍文, 等, 2007.天气学原理和方法[M].北京: 气象出版社.Zhu Q G, Lin J R, Shou S W, et al, 2007.Principles and methods of synoptic science[M].Beijing: Meteorological Press.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
|
朱蓉, 王阳, 向洋, 等, 2021.中国风能资源气候特征和开发潜力研究[J].太阳能学报, 42(6): 409-418.DOI: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2020-0130.Zhu R ,
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 PDF(12553 KB)
PDF(12553 KB)
 图1 不同类型大风发生站次占比(单位: %)
图1 不同类型大风发生站次占比(单位: %) 图2 云南125个国家站2013 -2021年发生大风次数(彩色圆点, 单位: 次数)叠加地形(填色, 单位: m)(a)、 发生热低压大风次数(b, 单位: 次数)、 2013 -2021年2 -4月15:00海平面气压平均值(等值线和彩色区, c, 单位: hPa)和相对整个研究时段15:00海平面气压异常值(等值线和彩色区, d, 单位: hPa)
图2 云南125个国家站2013 -2021年发生大风次数(彩色圆点, 单位: 次数)叠加地形(填色, 单位: m)(a)、 发生热低压大风次数(b, 单位: 次数)、 2013 -2021年2 -4月15:00海平面气压平均值(等值线和彩色区, c, 单位: hPa)和相对整个研究时段15:00海平面气压异常值(等值线和彩色区, d, 单位: hPa) 图3 2021年3月31日08:00 -19:59云南国家站17 m·s-1及以上大风(a, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 08:00 500 hPa风场(b, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 15:00 FY-2H-TBB(c, 单位: ℃)、 15:00 500 hPa垂直速度(d, 单位: Pa·s-1)及2021年3月31日08:00至4月1日08:00逐3 h昆明站地面气压演变(e, 单位: hPa)
图3 2021年3月31日08:00 -19:59云南国家站17 m·s-1及以上大风(a, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 08:00 500 hPa风场(b, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 15:00 FY-2H-TBB(c, 单位: ℃)、 15:00 500 hPa垂直速度(d, 单位: Pa·s-1)及2021年3月31日08:00至4月1日08:00逐3 h昆明站地面气压演变(e, 单位: hPa) 图4 云南125个国家站2013 -2021年发生雷暴大风次数(a, 单位: 次数)和冷空气大风次数(彩色圆点, 单位: 次数)叠加地形(填色, 单位: m)以及进入云南的冷空气常见路径(蓝线箭头)(b)
图4 云南125个国家站2013 -2021年发生雷暴大风次数(a, 单位: 次数)和冷空气大风次数(彩色圆点, 单位: 次数)叠加地形(填色, 单位: m)以及进入云南的冷空气常见路径(蓝线箭头)(b) 图5 云南125个国家站2013 -2021年发生南支槽前大风次数(a, 单位: 次数)、 2020年3月3日08:00 500 hPa风场(b, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 2020年3月3日17:00 -17:59区域站17 m·s-1及以上大风(风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加17:00 FY-2H-TBB(填色, 单位: ℃)(c)和2020年3月3日17:03昆明雷达0.5°仰角反射率因子(d, 单位: dBZ)
图5 云南125个国家站2013 -2021年发生南支槽前大风次数(a, 单位: 次数)、 2020年3月3日08:00 500 hPa风场(b, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 2020年3月3日17:00 -17:59区域站17 m·s-1及以上大风(风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加17:00 FY-2H-TBB(填色, 单位: ℃)(c)和2020年3月3日17:03昆明雷达0.5°仰角反射率因子(d, 单位: dBZ) 图6 2013年4月6日08:00 500 hPa风场实况(a, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 2013年4月6日14:00 -15:59国家站大风(风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加2013年4月6日14:30 FY-2F-TBB(填色, 单位: ℃)(b)、 2021年8月1日20:00 500 hPa风场实况(c, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 2021年8月1日17:00 -18:59国家站大风(风羽, 单位: m·s-1)及所有台风大风发生时台风中心位置(黑色圆点, d)、 2018年11月27日08:00 (e)和20:00 (f) 500 hPa风场实况(风羽, 单位: m·s-1), 20:00实况叠加13:00 -15:59国家站大风(f, 红色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)
图6 2013年4月6日08:00 500 hPa风场实况(a, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 2013年4月6日14:00 -15:59国家站大风(风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加2013年4月6日14:30 FY-2F-TBB(填色, 单位: ℃)(b)、 2021年8月1日20:00 500 hPa风场实况(c, 风羽, 单位: m·s-1)、 2021年8月1日17:00 -18:59国家站大风(风羽, 单位: m·s-1)及所有台风大风发生时台风中心位置(黑色圆点, d)、 2018年11月27日08:00 (e)和20:00 (f) 500 hPa风场实况(风羽, 单位: m·s-1), 20:00实况叠加13:00 -15:59国家站大风(f, 红色风羽, 单位: m·s-1) 图7 所有大风和不同类型大风风向玫瑰图
图7 所有大风和不同类型大风风向玫瑰图 图8 所有大风和不同类型大风不同等级大风发生比例(单位: %)
图8 所有大风和不同类型大风不同等级大风发生比例(单位: %) 图9 所有大风和不同类型大风发生站次年变化
图9 所有大风和不同类型大风发生站次年变化 图10 雷暴大风日数年变化
图10 雷暴大风日数年变化 图11 2015年4月23日08:00 500 hPa风场实况(蓝色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加17:00 -17:59普洱区域站7级及以上大风(风速≥13.9 m·s-1, 红色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)(a)、 2015年8月11日08:00 500 hPa风场实况(蓝色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加18:00 -18:59普洱区域站7级及以上大风(红色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)(b)、 2015年4月23日17:32普洱0.5°仰角反射率因子(c, 单位: dBZ)、 2015年8月11日18:52普洱0.5°仰角反射率因子(d, 单位: dBZ)、 2015年4月23日08:00普洱订正探空(e)及2015年8月11日08:00普洱订正探空(f)
图11 2015年4月23日08:00 500 hPa风场实况(蓝色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加17:00 -17:59普洱区域站7级及以上大风(风速≥13.9 m·s-1, 红色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)(a)、 2015年8月11日08:00 500 hPa风场实况(蓝色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)叠加18:00 -18:59普洱区域站7级及以上大风(红色风羽, 单位: m·s-1)(b)、 2015年4月23日17:32普洱0.5°仰角反射率因子(c, 单位: dBZ)、 2015年8月11日18:52普洱0.5°仰角反射率因子(d, 单位: dBZ)、 2015年4月23日08:00普洱订正探空(e)及2015年8月11日08:00普洱订正探空(f) 图12 所有大风和不同类型大风发生站次日变化
图12 所有大风和不同类型大风发生站次日变化 表1 所有大风和不同类型大风风速平均值、 25%和75%分位值、 最大值
表1 所有大风和不同类型大风风速平均值、 25%和75%分位值、 最大值 表2 所有大风和不同类型大风发生站次时间变化特征
表2 所有大风和不同类型大风发生站次时间变化特征/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |