1 引言
2 资料来源与方法介绍
2.1 尘卷风发生的热力学阈值
2.2 尘卷风起沙量
2.3 实测资料
3 柴达木盆地尘卷风特征
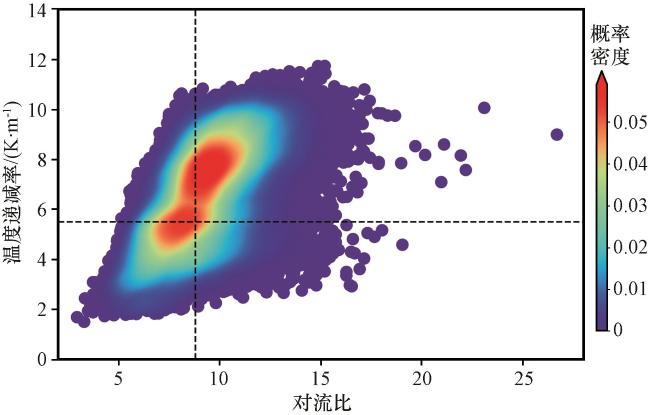
3.1 尘卷风发生的热力学阈值
图1 柴达木盆地夏季对流比(w */u *)和近地面温度递减率(LR)的联合概率密度虚线代表平均值 Fig.1 Joint probability density plot of convective ratio (w */u *) and near-surface temperature lapse rate (LR) in summer in the Qaidam Basin.Dashed lines represent mean values |
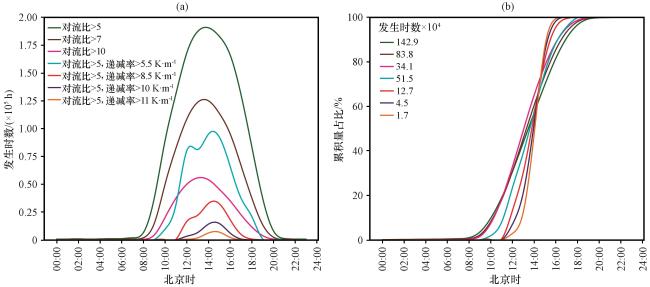
图2 柴达木盆地不同对流比(w */u *)和近地面温度递减率(LR)阈值对应的1991 -2020年的年平均尘卷风发生时数(PDDPhours)的日变化(a)和PDDPhours累积量占比的日变化(b)Fig.2 Diurnal changes in the annual mean number of PDDPhours during 1991 to 2020 (a) and the cumulative proportion of PDDPhours (b) using different convective ratio (w */u *) and near-surface temperature lapse rate (LR) criteria in the Qaidam Basin |
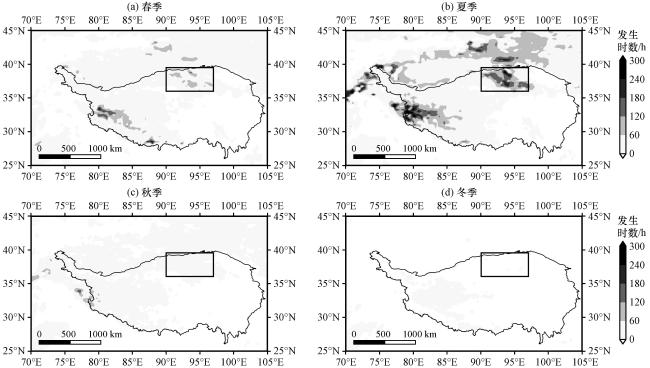
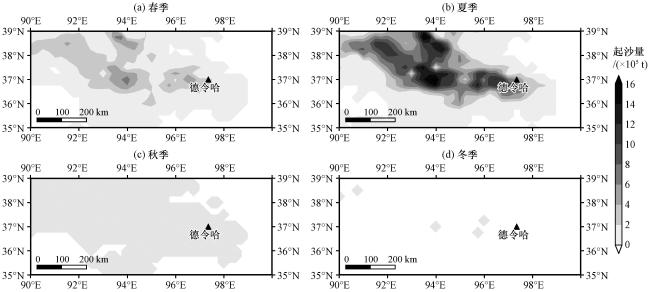
3.2 尘卷风发生时数和起沙量的分布特征
图3 满足热力学阈值条件w */u *>5、 LR > 10 K·m-1的1991 -2020年春季(a)、 夏季(b)、 秋季(c)、 冬季(d)PDDPhours 的空间分布(单位: h)黑线为海拔为3000 m等值线, 黑色方框表示柴达木盆地 Fig.3 Spatial distribution of PDDPhours under the criteria of w */u *>5, LR > 10 K·m-1 for a time period from 1991 to 2020 in spring(a), summer(b), autumn(c)and winter(d).Unit: h.Black lines represent the altitude of 3000 m, and the black box indicates the location of Qaidam Basin |
图4 根据PDDPhours估算的 1991-2020年春季(a)、 夏季(b)、 秋季(c)、 冬季(d)柴达木盆地尘卷风平均起沙量的空间分布(单位: ×105 t)黑色三角形代表德令哈 Fig.4 Spatial distribution of dust emission estimated by PDDPhours in the Qaidam Basin for a time period from 1991 to 2020 in spring(a), summer(b), autumn(c) and winter(d).Unit: ×105 t.The black triangle stands for the location of Delingha |
3.3 热力学阈值及尘卷风发生时数的变化趋势
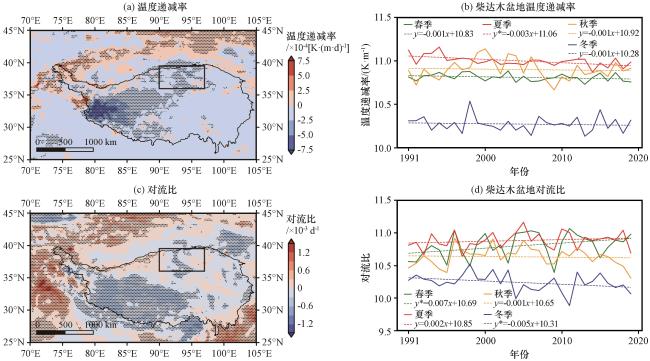
图5 1991 -2020年青藏高原夏季近地面温度递减率LR[a, 单位: ×10-4 K·(m·d)-1]、 对流比w */u *(c, 单位: ×10-3 d-1)的变化趋势和不同季节柴达木盆地温度递减率LR(b)、 对流比w */u *(d)的时间变化 (a~c)中黑线为海拔3000 m的等值线, 黑色方框表示柴达木盆地, 黑色打点区域代表通过了0.05的信度检验; (b~d)中*号代表通过了0.05的信度检验Fig.5 The trend of surface temperature lapse rate LR [a, unit: ×10-4 K·(m·d)-1], convective ratio (w */u *) (c, unit: ×10-3 d-1)over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau during the time period of 1991 -2020.And the time series of temperature lapse rate LR (b) and convective ratio (w */u *) (d) at Qaidam Basin in different seasons.Black lines in (a~c) represent the altitude of 3000 m, and the black box indicates the location of Qaidam Basin., and the black dotted area represents a reliability test of 0.05.Stars in the equation in (b~d) denote the significant values at the 95% confidence level |
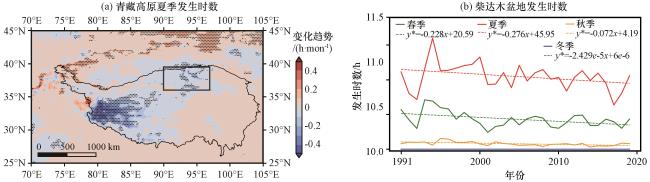
图6 1991 -2020年青藏高原夏季发生时数PDDPhours的变化趋势(a, 单位: h·mon-1)和不同季节柴达木盆地发生时数的时间变化(b, 单位: h)(a)中黑线为海拔3000 m的等值线, 黑色方框表示柴达木盆地, 黑色打点区域代表通过了0.05的信度检验; (b)中*号代表通过了0.05的信度检验Fig.6 The spatial distribution of PDDPhours trend over the Tibetan Plateau (a, unit: h·mon-1) and the time series of PDDPhours in the Qaidam Basin in different seasons during the time period of 1991 -2020 (b, unit: h).Black lines in (a) represent the altitude of 3000 m, the black box indicates the location of Qaidam Basin, and the black dotted area represents a reliability test of 0.05.Stars in the equation in (b) denote the significant values at the 95% confidence level |
3.4 实测资料分析
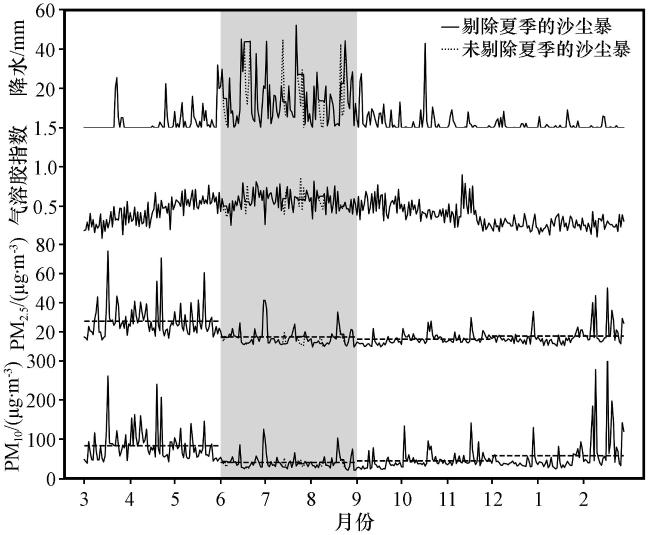
图7 2016 -2020年德令哈紫外吸收性气溶胶指数、 德令哈气象站累计日降水量, 以及德令哈空气质量监测站日平均PM2.5和PM10随时间的变化阴影表示夏季, 黑色虚线代表各季节平均值 Fig.7 Time series of UV aerosol index at Delingha, cumulative daily precipitation at Delingha meteorological station, PM2.5 and PM10 at Delingha air quality monitoring station from 2016 to 2020.Summer is highlighted in the shaded gray, and black dashed lines represent the seasonal average value |