1 引言
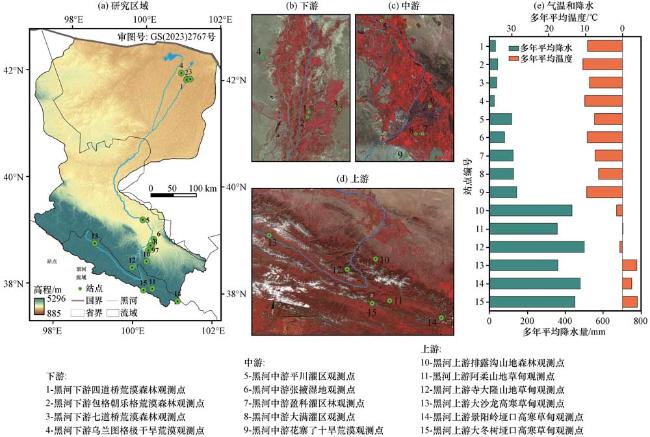
2 研究区概况
2 数据来源和方法介绍
2.1 蒸散发数据
表1 蒸散发产品信息Table 1 Evapotranspiration product information |
| 产品 | 时间分辨率 | 空间分辨率 | 时间跨度 | 空间范围 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSEBop | 10天 | 1000 m | 2013 -2023年 | 全球 | https: //earlywarning.usgs.gov/ |
| GLEAM | 年/月 | 0.25° | 1980 -2023年 | 全球 | https: //www.gleam.eu/ |
| MOD16 | 8天 | 500 m | 2000 -2023年 | 全球 | https: //developers.google.com/ |
| PML_V2 | 8天 | 500 m | 2002 -2020年 | 全球 | https: //poles.tpdc.ac.cn/ |
| GLASS | 8天 | 0.05° | 2001 -2018年 | 全球 | http: //www.geodata.cn/ |
| ETMonitor | 月 | 1000 m | 2000 -2019年 | 全球 | https: //poles.tpdc.ac.cn/ |
2.2 涡动协方差通量数据
表2 涡度通量观测站及数据信息Table 2 Eddy flux observatories and data information |
| 序号 | 行政区 | 观测点位置 | 经度 /°E | 纬度 /°N | 高程 /m | 年均降雨 /mm | 年均气温 /℃ | 生态系统类型 | 植被群系 | 时间 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 内蒙古额济纳旗 | 四道桥 | 101.14 | 42.00 | 873 | 30 | 9.5 | 荒漠森林 | 柽柳纯林 | 2014 -2023年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
| 2 | 内蒙古额济纳旗 | 包格朝乐格 | 101.13 | 41.99 | 874 | 42.39 | 10.74 | 荒漠森林 | 胡杨+柽柳混交林 | 2014 -2023年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
| 3 | 内蒙古额济纳旗 | 七道桥 | 101.23 | 42.00 | 931 | 36.5 | 9 | 荒漠森林 | 胡杨纯林 | 2014 -2016年 | Yu et al, 2019 |
| 4 | 内蒙古额济纳旗 | 乌兰图格 | 100.99 | 42.11 | 1054 | 24.5 | 10.22 | 极干旱荒漠 | 红砂 | 2016 -2023年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
| 5 | 甘肃张掖 | 平川灌区 | 100.14 | 39.33 | 1381 | 117 | 7.6 | 农田 | 玉米 | 2012 -2015年 | 吉喜斌等, 2023 |
| 6 | 甘肃张掖 | 张掖湿地 | 100.45 | 38.98 | 1460 | 77.91 | 9.6 | 沼泽湿地 | 芦苇等 | 2013 -2022年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
| 7 | 甘肃张掖 | 盈科灌区 | 100.41 | 38.86 | 1519 | 124 | 7.4 | 农田 | 玉米 | 2008 -2011年 | 刘强等, 2015 |
| 8 | 甘肃张掖 | 大满灌区 | 100.37 | 38.86 | 1556 | 126.52 | 6.47 | 农田 | 玉米 | 2013 -2023年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
| 9 | 甘肃张掖 | 花寨子 | 100.32 | 38.77 | 1731 | 142.22 | 9.69 | 干旱荒漠 | 盐爪爪 | 2015 -2023年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
| 10 | 甘肃张掖 | 排露沟 | 100.29 | 38.55 | 2762 | 435.5 | 1.6 | 山地森林 | 青海云杉 | 2018 -2020年 | 郝玉莲, 2024 |
| 11 | 青海祁连县 | 阿柔 | 100.46 | 38.05 | 3033 | 357.57 | -0.12 | 山地草甸 | 垂穗披碱草+短颖鹅观草 | 2013 -2023年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
| 12 | 甘肃肃南县 | 寺大隆 | 99.93 | 38.43 | 3146 | 542.4 | 0.2 | 山地草甸 | 苔草+垂穗披碱草 | 2014 -2018年 | 高云飞, 2020 |
| 13 | 青海祁连县 | 大沙龙 | 98.94 | 38.84 | 3739 | 360.48 | -3.89 | 高寒草甸 | 西藏蒿草+喜马拉雅蒿草+矮生蒿草 | 2014 -2023年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
| 14 | 青海祁连县 | 景阳岭垭口 | 101.12 | 37.84 | 3750 | 478.5 | -2.52 | 高寒草甸 | 唐古拉红景天+青藏薹草+矮生蒿草 | 2018~2023年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
| 15 | 青海祁连县 | 大冬树垭口 | 100.24 | 38.01 | 4148 | 450.5 | -4.03 | 高寒草甸 | 红景天+青藏薹草 | 2016~2023年 | 刘绍民等, 2023 |
2.3 数据处理
2.4 研究方法
2.4.1 蒸散发计算
2.4.2 评价指标
3 结果与分析
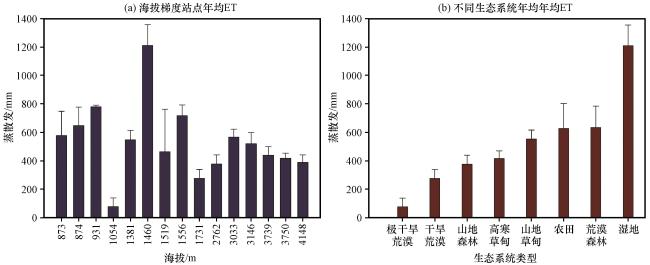
3.1 站点蒸散发数据分析
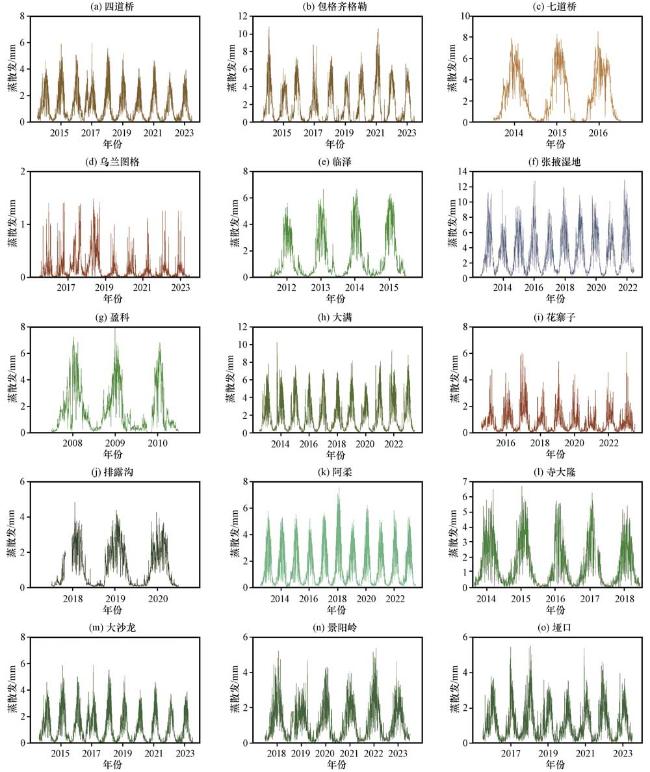
图2 黑河流域15个涡度通量站点日蒸散发的年变化编号见图1 Fig.2 Annual variation of daily evapotranspiration at 15 eddy flux stations in the Heihe River Basin.See Fig.1 for numbers |
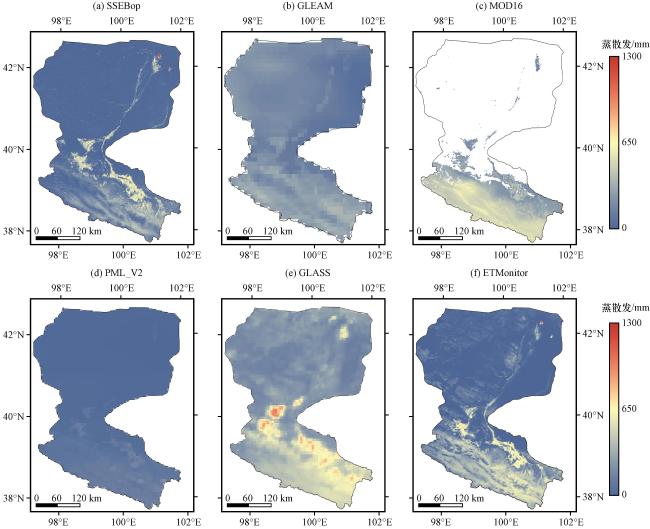
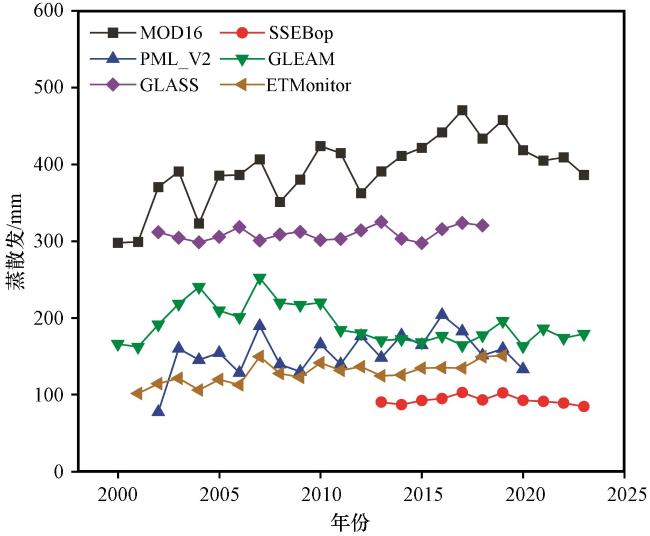
3.2 遥感蒸散发产品时空分布
3.3 蒸散发产品整体精度评价
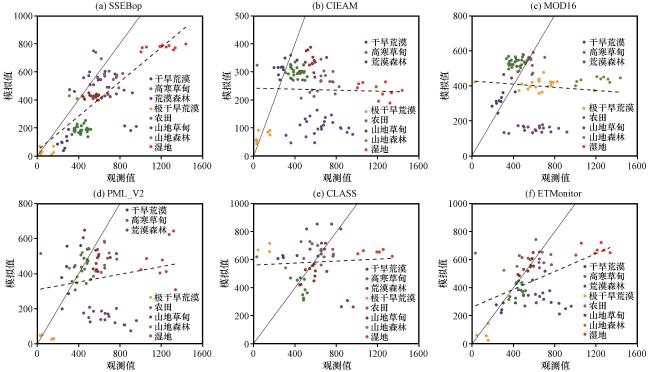
图6 地面站点与蒸散发产品拟合结果Fig.6 Fitting results of ground station and evapotranspiration product |
表3 蒸散发产品各指标Table 3 Indicators of evapotranspiration products |
| 产品 | 拟合方程 | 显著性 | RMSE/(mm·a-1) | Bias | MAE/(mm·a-1) | R² |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSEBop | y=0.612x+38.438 | P<0.01 | 251.99 | -178.42 | 200.65 | 0.63 |
| GLEAM | y=-0.009x+241.65 | p>0.05 | 442.31 | -317.49 | 332.79 | 0.0007 |
| MOD16 | y=-0.045x+427.80 | p>0.05 | 360.47 | -180.33 | 263.15 | 0.0068 |
| PML_V2 | y=0.11x+309.15 | p>0.05 | 363.99 | -204.97 | 259.72 | 0.033 |
| GLASS | y=0.036x+562.36 | p>0.05 | 296.51 | -22.57 | 212.09 | 0.004 |
| ETMonitor | y=0.318x+262.81 | P<0.01 | 275.47 | -140.37 | 190.03 | 0.26 |
4 讨论
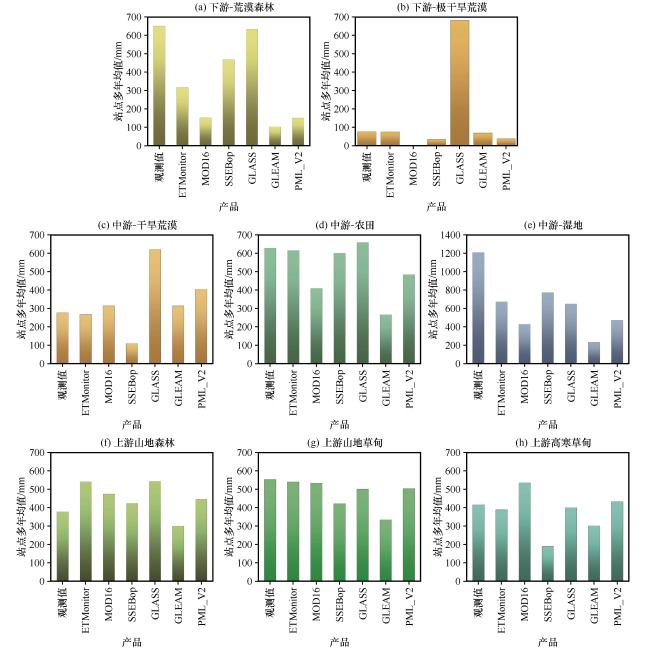
图7 不同生态系统各蒸散发产品对比(a)荒漠森林, (b)极干旱荒漠, (c)干旱荒漠, (d)农田, (e)湿地, (f)山地森林, (g)山地草甸, (h)高寒草甸 Fig.7 Comparison of evapotranspiration products in different ecosystems.(a) Desert forest, (b) extremely arid desert, (c) arid desert, (d) farmland, (e) wetland, (f) mountain forest, (g) mountain meadow, (h) alpine meadow |
表4 不同生态系统各蒸散发产品各指标Table 4 Different ecosystems have their own evapotranspiration products |
| 产品 | SSEBop | GLEAM | MOD16 | PML_V2 | GLASS | ETMonitor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农田 | 拟合方程 | y=-0.58x+1002.1 | y=0.08x+210.34 | y=0.09x+349.35 | y=0.27x+310.07 | y=-0.19x+780.02 | y=-0.12x+693.5 |
| R² | R²=0.5004 | R²=0.0514 | R²=0.1013 | R²=0.177 | R²=0.1434 | R²=0.0574 | |
| 显著性 | <0.01 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | |
| 湿地 | 拟合方程 | y=0.06x+707.98 | y=-0.08x+331.85 | y=0.07x+346.7 | y=0.16x+284.3 | y=-0.03x+692.69 | y=0.01x+664.86 |
| R² | R²=0.2438 | R²=0.2015 | R²=0.1559 | R²=0.0273 | R²=0.0605 | R²=0.0006 | |
| 显著性 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | |
| 干旱荒漠 | 拟合方程 | y=0.57x-47.08 | y=0.21x+255.69 | y=0.42x+196.35 | y=3.88x+330.95 | y=0.10x+591.85 | y=0.19x+210.51 |
| R² | R²=0.4703 | R²=0.3086 | R²=0.5109 | R²=0.0017 | R²=0.4851 | R²=0.1637 | |
| 显著性 | <0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | |
| 极干旱荒漠 | 拟合方程 | y=0.002x+33.46 | y=0.21x+52.57 | 无数据 | y=-0.18x+55.65 | y=0.16x+663.11 | y=0.17x+52.93 |
| R² | R²=3E-05 | R²=0.4758 | R²=0.9033 | R²=0.1082 | R²=0.0335 | ||
| 显著性 | >0.05 | 0.05 | 0.01 | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||
| 荒漠森林 | 拟合方程 | y=-0.34x+680.73 | y=0.05x+74.57 | y=0.01x+145.88 | y=-0.16x+254.74 | y=-0.92x+1272 | y=-0.21x+454.11 |
| R² | R²=0.1859 | R²=0.0507 | R²=0.0074 | R²=0.2657 | R²=0.1818 | R²=0.2535 | |
| 显著性 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | 0.05 | |
| 山地森林 | 拟合方程 | y=-0.02x+430.3 | y=0.02x+293.77 | y=0.32x+351.99 | y=0.60x+219.58 | 数据≤2 | 数据≤2 |
| R² | R²=0.0135 | R²=0.0435 | R²=0.3551 | R²=0.2903 | |||
| 显著性 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | |||
| 高寒草甸 | 拟合方程 | y=0.03x+177.71 | y=-0.10x+341.56 | y=0.07x+505.3 | y=0.53x+202.25 | y=-0.79x+767.46 | y=0.37x+220.07 |
| R² | R²=0.0033 | R²=0.0524 | R²=0.0318 | R²=0.1804 | R²=0.3541 | R²=0.163 | |
| 显著性 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | |
| 山地草甸 | 拟合方程 | y=-0.01x+427.12 | y=0.07x+298.23 | y=0.19x+429.36 | y=-0.62x+852.3 | y=0.35x+306.17 | y=0.23x+411.66 |
| R² | R²=0.0012 | R²=0.0173 | R²=0.0883 | R²=0.361 | R²=0.2457 | R²=0.0909 | |
| 显著性 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 |