1 引言
2 资料来源与方法介绍
2.1 资料来源
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 供热负荷数据预处理
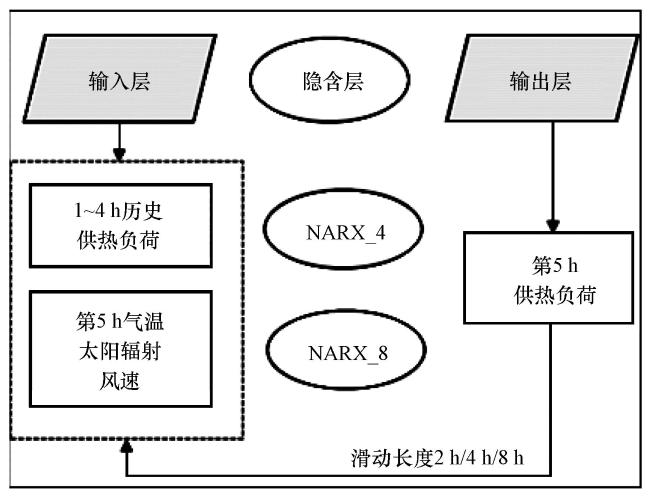
2.2.2 NARX神经网络模型数据集构建
表1 多要素数据集Table 1 Multi-factor datasets |
| 数据集 | 历史供热负荷 | 平均气温 | 太阳辐射 | 平均风速 | 相对湿度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数据集A | ○ | ○ | × | × | × |
| 数据集B | ○ | ○ | ○ | × | × |
| 数据集C | ○ | ○ | × | ○ | × |
| 数据集D | ○ | ○ | × | × | ○ |
| 数据集E | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | × |
| 数据集F | ○ | ○ | ○ | × | ○ |
| 数据集G | ○ | ○ | × | ○ | ○ |
| 数据集H | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
“○”表示该数据集包含该要素, “×”表示该数据集不包含该要素('○' indicates that the dataset contains the element; '×' indicates that the dataset does not contain the element) |
2.2.3 NARX神经网络模型训练数据归一化处理
2.2.4 NARX神经网络模型训练步骤及参数设置
表2 不同模型对应的滑动窗口长度和隐含层数量Table 2 Sliding window length and number of hidden layers for different hourly models |
| 滑动窗口长度/h | 4隐含层 | 8隐含层 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | NARX2_4 | NARX2_8 |
| 4 | NARX4_4 | NARX4_8 |
| 8 | NARX8_4 | NARX8_8 |
2.2.5 NARX神经网络模型评估方法
3 结果分析
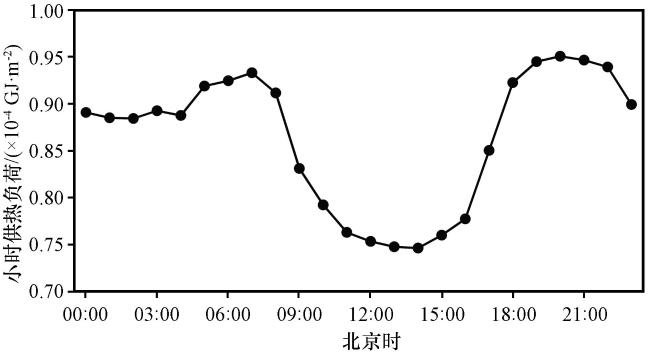
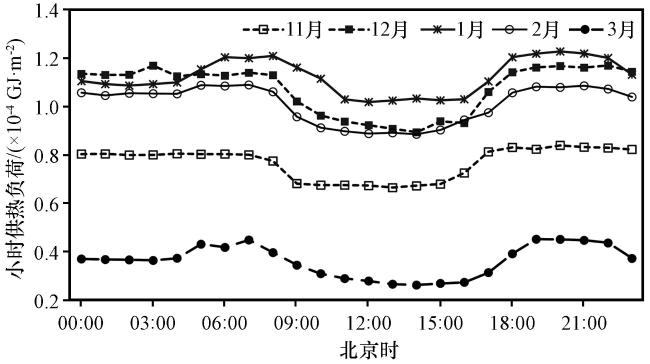
3.1 供热负荷的时间特征分析
3.2 供热负荷与气象因子的相关分析
表3 2021 -2022年采暖季各月逐小时气象要素和供热负荷的相关关系Table 3 Correlations between hourly meteorological factors and heating load for each month during the 2021 -2022 heating season |
| 月份 | 平均气温 | 相对湿度 | 太阳辐射 | 平均风速 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11月 | -0.659* | -0.154* | -0.204* | 0.122* |
| 12月 | -0.711* | -0.122* | -0.360* | 0.008 |
| 1月 | -0.343* | 0.325* | -0.304* | -0.135* |
| 2月 | -0.763* | 0.333* | -0.303* | -0.272* |
| 3月 | -0.574* | 0.079* | -0.310* | -0.160* |
*表示通过 的显著性检验(* indicates statistical significance at α=0.05) |
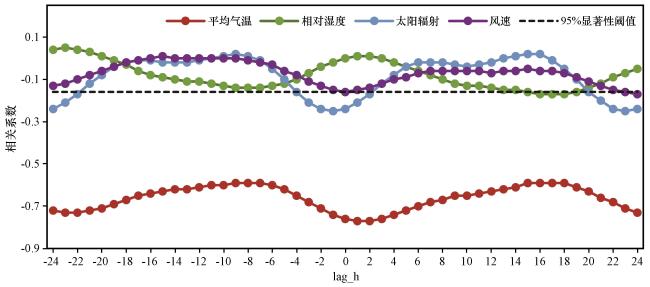
图4 2021 -2022年采暖季逐小时供热负荷与各气象要素的时滞相关系数其中横坐标表示超前24 h到滞后24 h, 0表示同时相关, 黑色虚线表示95%显著性检验的临界值 Fig.4 The lagged correlation coefficients of hourly heating load with various meteorological factors during the 2021 -2022 heating season.The horizontal axis represents a range from 24 hours ahead to 24 hours behind, with 0 indicating simultaneous correlation, and the black dashed line indicating the threshold for the 95% significance test |
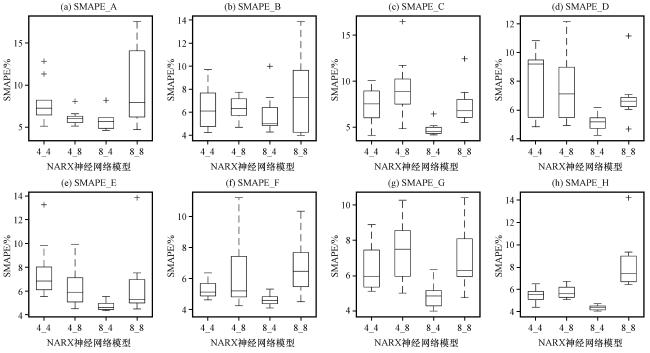
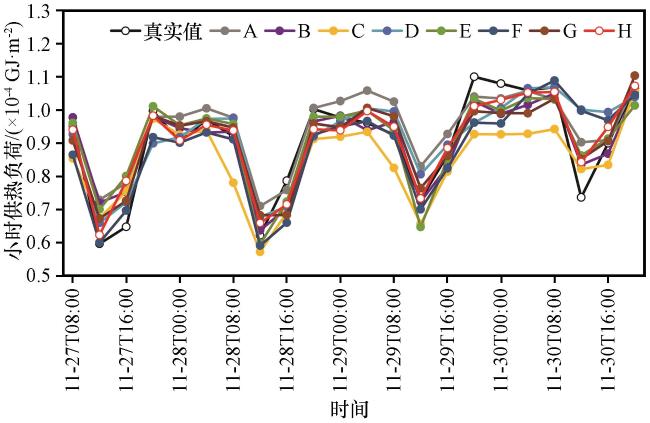
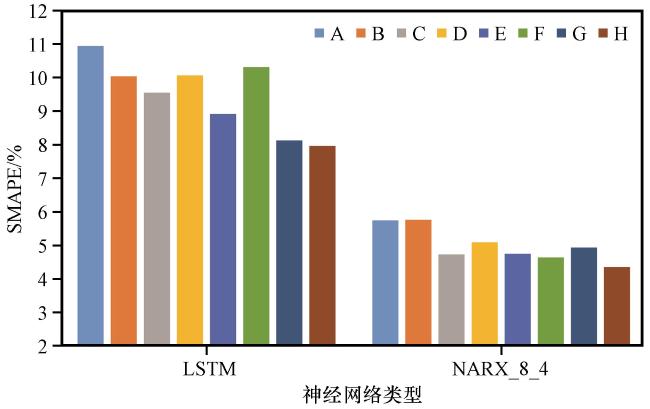
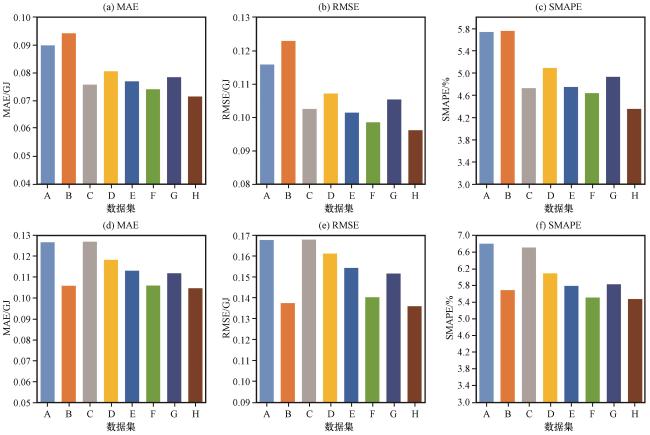
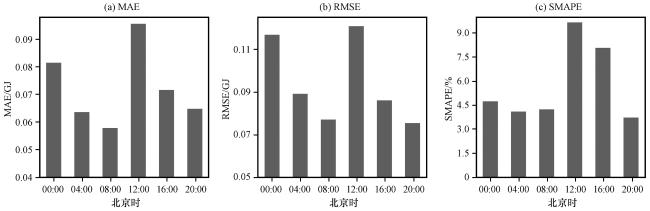
3.3 供热负荷预测模型实验结果
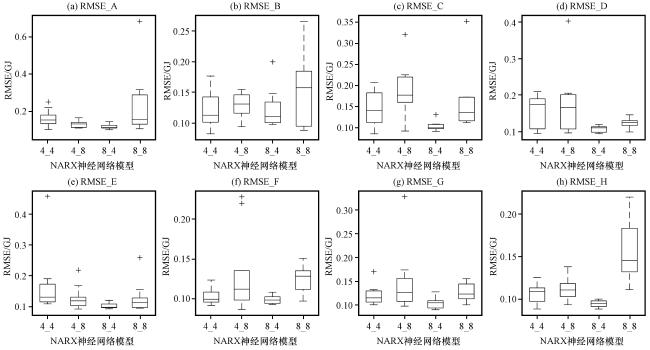
图5 供热负荷预测中使用不同数据集训练模型的均方根误差RMSE箱线图Fig.5 The box plot of root mean square error RMSE for the training of the heating load models using different datasets |
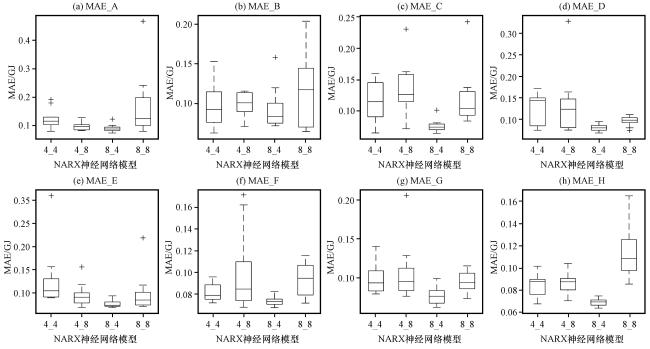
图6 供热负荷预测中使用不同数据集训练模型的平均绝对误差MAE箱线图Fig.6 The box plot of mean absolute error MAE for the training of the heating load models using different datasets |