1 引言
2 研究区域、 数据和方法
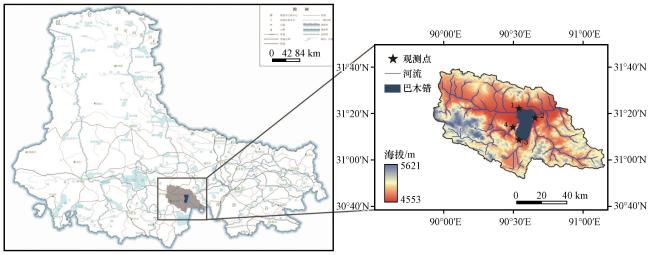
2.1 研究区域
2.2 研究数据
2.2.1 野外观测数据
表1 巴木错观测点观测内容及所用仪器Table 1 Observation contents and instruments used in Bamu Co |
| 观测点 | 观测要素 | 仪器型号 | 制造商 | 数据时段 | 分辨率 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 自动水位计 | HOBO-U20 | Onset HOBO | |||
| 自记翻斗式雨量筒 | HOBO RG3-M | Onset HOBO | 2022 -2023年 | 30 min | mm | |
| 2 | 自动水位计 | HOBO-U20 | Onset HOBO | 2022 -2023年 | 30 min | cm |
| 自记翻斗式雨量筒 | HOBO RG3-M | Onset HOBO | 2021年 | 30 min | mm | |
| 涡动观测 | CSAT3 | Campbell | 2021年 | 30 min | ||
| 3 | 自动水位计 | HOBO-U20 | Onset HOBO | 2023年 | 30 min | cm |
| 自记翻斗式雨量筒 | HOBO RG3-M | Onset HOBO | ||||
| 4 | 自动水位计 | HOBO-U20 | Onset HOBO | 2022年 | 30 min | cm |
| 自记翻斗式雨量筒 | HOBO RG3-M | Onset HOBO | 2021年、 2023年 | 30 min | mm | |
| 人工测流 | LCY-001型便携式流速仪 | 重庆华正 | 2021年8月16日、 2022年7月19日、 2023年7月20 -23日、 2023年10月26日 | 2 h | m·s-1 | |
| 雷达流量计 | 300W-QX 系列 | 西安鹰格 | 2021 -2023年 | 30 min | m3·s-1 |
2.2.2 气象要素数据
2.2.3 第三极地区高分辨率地面气象要素驱动数据集(TPMFD)
2.3 研究方法
2.3.1 水量平衡方程
2.3.2 入湖径流量计算方法
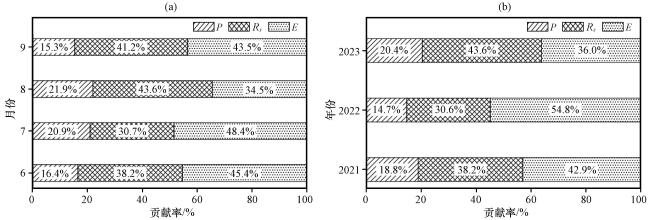
2.3.3 水量平衡因子贡献量化法
3 结果分析
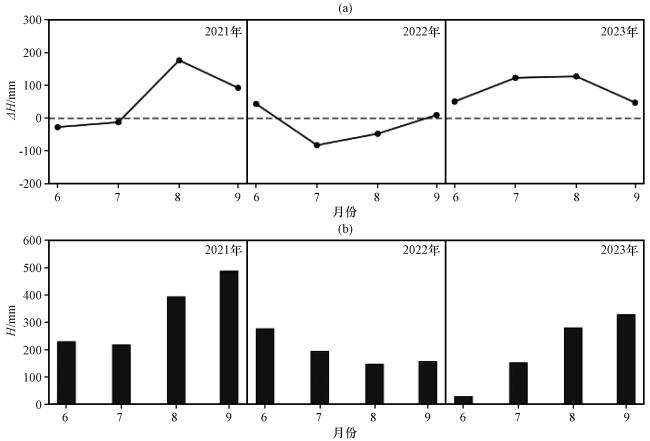
3.1 水量收支变化特征
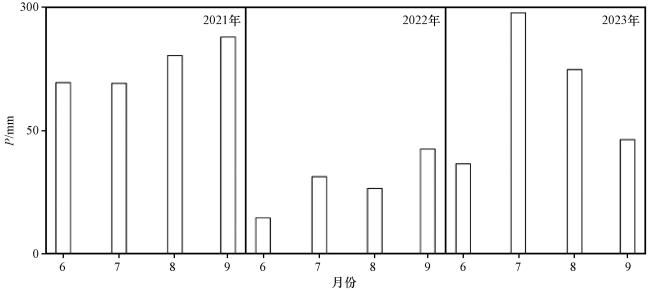
3.1.1 湖面降水的时序特征
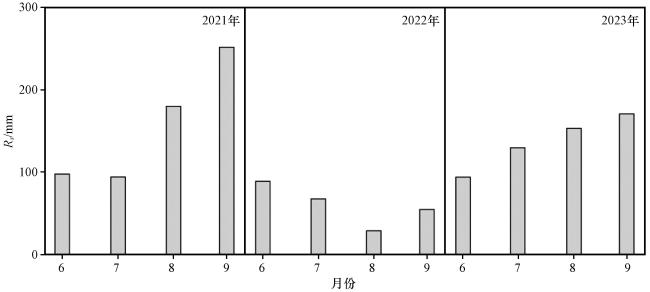
3.1.2 入湖径流的动态特征
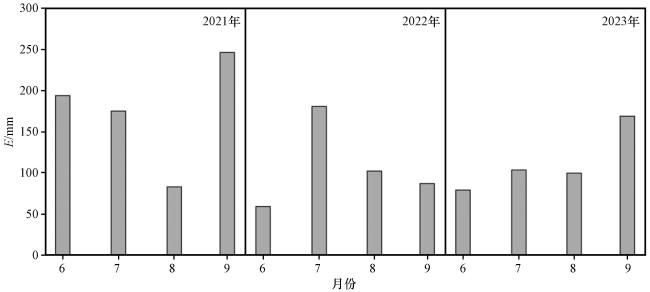
3.1.3 湖面蒸发的变化特征
3.1.4 水位变化的时序差异
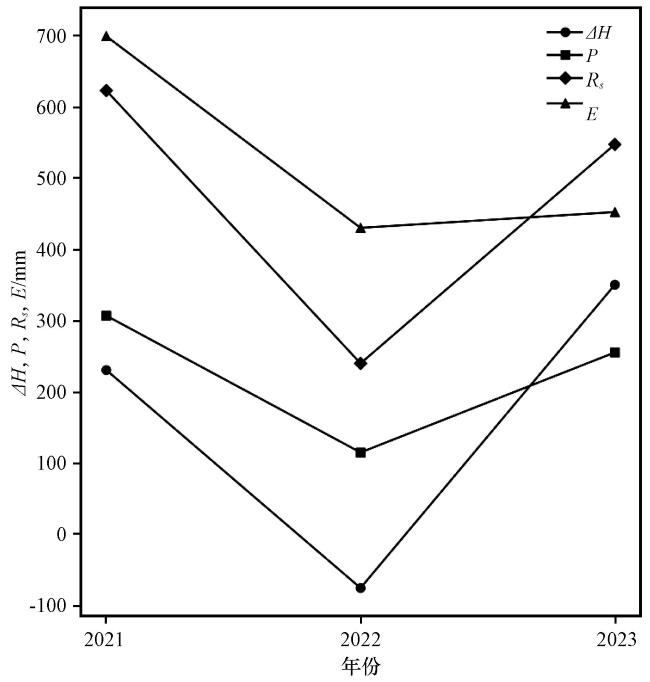
3.2 水量平衡要素对水位变化的贡献
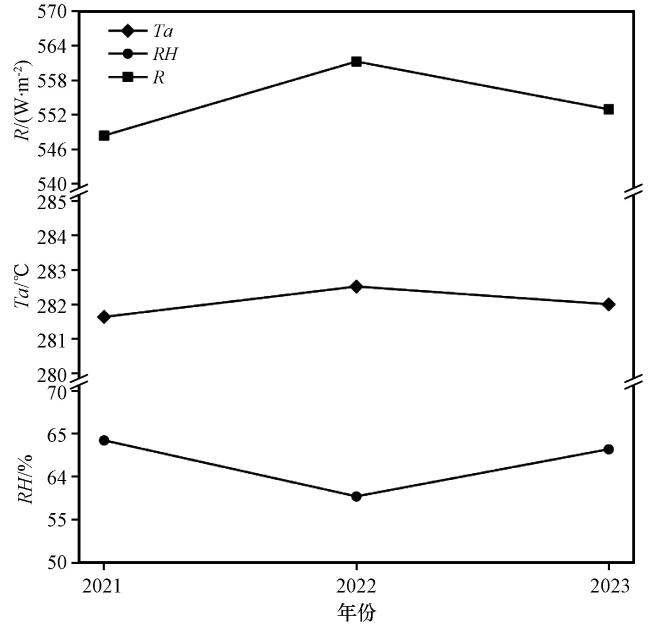
3.3 气象要素对巴木错水位变化的影响
图7 巴木错湖泊∆H和水量平衡要素的年际变化Fig.7 Interannual variation of water level change (∆H) and water balance components (P, , E) in Bamu Co |
表2 巴木错 E/P 比值和流域气象要素的年际变化Table 2 Interannual variability of the E/P ratio and basin meteorological elements in Bamu Co |
| 年份 | ∆H/mm | E/P | 气象要素变化 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | +231 | 2.28 | Ta: 中等; RH: 高; R: 中等 |
| 2022 | -75 | 3.74 | Ta: +0.88 K; RH: -6.5%; R: +2.3% |
| 2023 | +350.6 | 1.77 | Ta: -0.52 K; RH: +5.5%; R: -1.5% |