1 引言
2 数据
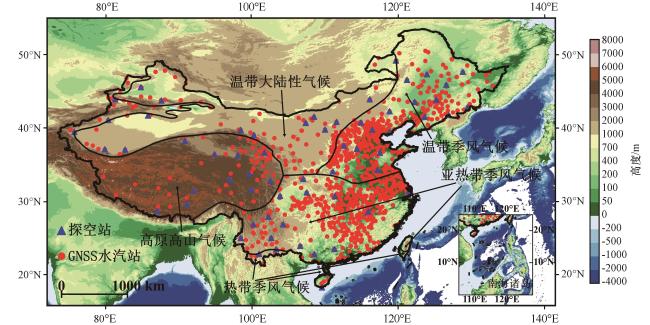
2.1 地基GNSS观测
2.2 探空观测
2.3 ERA5再分析资料
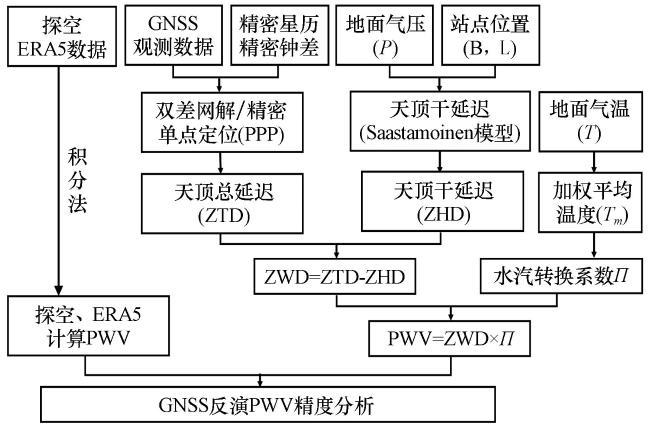
3 数据处理方法
3.1 地基GNSS数据处理
3.1.1 天顶对流层延迟反演
表1 GNSS数据处理策略Table 1 GNSS data processing strategies |
| 观测值 | 观测值 | GPS卫星LC、 PC组合观测值 |
|---|---|---|
| 高度截止角 | 7 | |
| 加权策略 | ||
| 误差改正 | 相位缠绕 | 改正 |
| 相位中心变化 | IGS14模型 | |
| 大气负荷 | 不考虑 | |
| 潮汐改正 | 固体潮、 极移潮汐、 海洋潮汐 | |
| 相对论改正 | 改正 | |
| 先验温度气压模型 | GPT2模型 | |
| 参数估计 | 卫星轨道 | 固定(IGS Final 产品) |
| 对流层随机模型 | 分段常数(0.5 h) 段间随机游走(20 mm/ ) | |
| 投影函数 | GMF | |
| 测站坐标 | 日常数 | |
| 参考框架 | 参考框架 | ITRF14(SOPAC动态更新) |
| 参考站(双差解) | 参考站(双差解) | IISC、 KIT3、 POL2、 SELE、 NVSK、 ULAB、 KHAJ、 DAEJ、 GUAM、 AIRA、 TSKB、 TWTF、 PIMO、 NTUS、 PBRI |
| 滑动窗口长度 | 滑动窗口长度 | 12 h |
3.1.2 地基GNSS大气可降水量计算
3.2 探空与ERA5再分析资料的PWV计算
4 GNSS大气可降水量反演精度对比分析
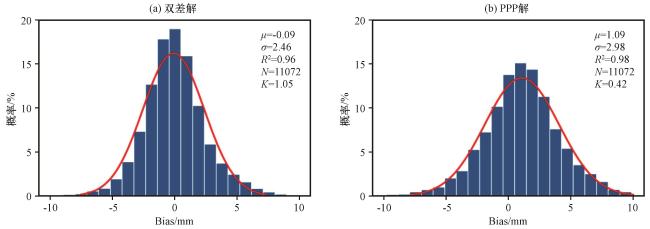
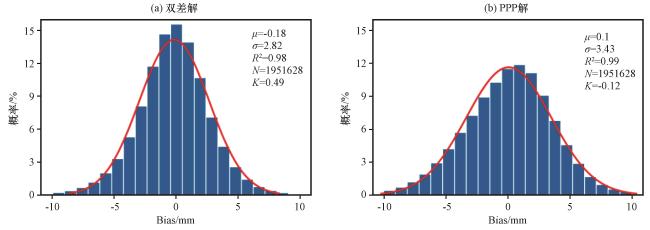
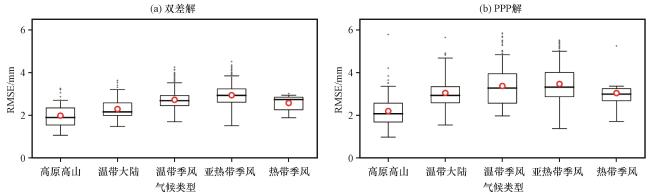
4.1 基于探空的GNSS-PWV反演精度对比分析
表2 基于探空参考值的PWV反演精度评估结果Table 2 Evaluation results of PWV inversion accuracy based on radiosonde reference values |
| 解算方法 | Bias/mm | RMSE/mm | 相关系数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | mean | median | min | max | mean | mean | ||
| 高原高山气候 | 双差解 | -1.8 | 4.4 | 0.1 | -0.4 | 1.1 | 4.6 | 1.8 | 0.96 |
| PPP解 | 0.1 | 6.3 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 0.96 | |
| 温带大陆性气候 | 双差解 | -2.9 | 1.8 | -0.1 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 3.9 | 2.2 | 0.96 |
| PPP解 | -2.5 | 4.5 | 1.7 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 5.1 | 3.3 | 0.95 | |
| 温带季风气候 | 双差解 | -2.0 | 1.9 | -0.2 | -0.1 | 1.5 | 3.7 | 2.6 | 0.98 |
| PPP解 | -4.7 | 5.7 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 6.8 | 3.6 | 0.97 | |
| 亚热带季风气候 | 双差解 | -1.8 | 4.3 | 0.2 | -0.3 | 1.4 | 5.2 | 2.8 | 0.94 |
| PPP解 | -3.0 | 3.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 6.1 | 3.2 | 0.92 | |
| 热带季风气候 | 双差解 | -1.1 | -0.5 | -0.8 | -0.8 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 2.7 | 0.90 |
| PPP解 | -1.6 | 1.4 | -0.1 | -0.1 | 2.5 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 0.92 | |
| 中国区域 | 双差解 | -2.9 | 4.3 | -0.1 | -0.3 | 1.1 | 5.2 | 2.4 | 0.96 |
| PPP解 | -4.7 | 6.3 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 6.8 | 3.1 | 0.95 | |
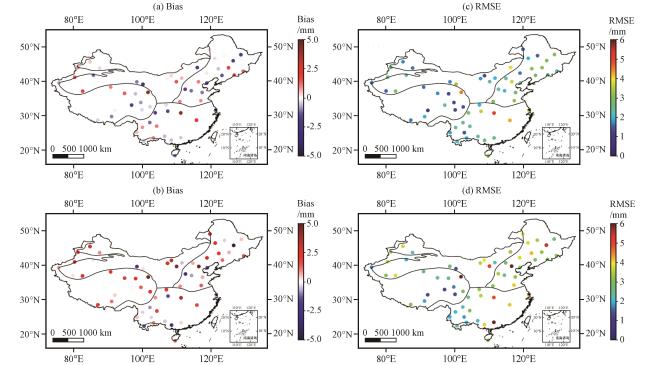
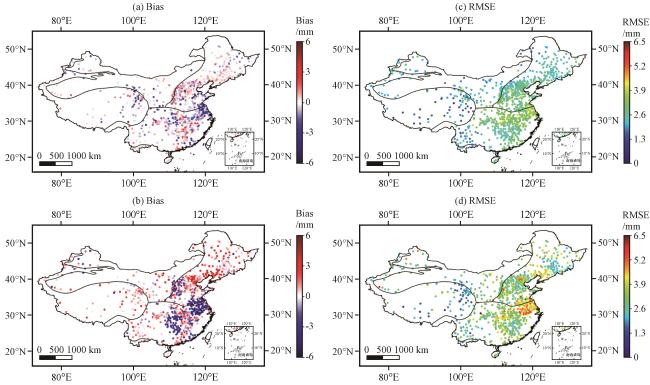
图4 GNSS-PWV与RS-PWV的Bias(单位:mm)、 RMSE(单位:mm)区域分布(a)、 (c)双差解与探空资料的对比结果, (b)、 (d)PPP解与探空资料的对比结果 Fig.4 Bias (unit:mm) and RMSE (unit:mm) regional distribution of GNSS-PWV and RS-PWV.(a), (c) the comparison results between double-difference network solution and radiosonde data, (b), (d) the comparison results between PPP solution and radiosonde data |
4.2 基于ERA5再分析资料的GNSS-PWV反演精度对比分析
表3 基于ERA5参考值的PWV反演精度评估结果Table 3 Evaluation results of PWV inversion accuracy based on ERA5 reference values |
| 解算方法 | Bias/mm | RMSE/mm | 相关系数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | mean | median | min | max | mean | mean | ||
| 高原高山气候 | 双差解 | -2.9 | 1.9 | -0.5 | -0.5 | 1.1 | 3.3 | 2.0 | 0.93 |
| PPP解 | -3.0 | 3.4 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 5.8 | 2.2 | 0.91 | |
| 温带大陆性气候 | 双差解 | -3.2 | 2.2 | -0.2 | -0.1 | 1.5 | 3.6 | 2.3 | 0.96 |
| PPP解 | -4.8 | 4.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 5.7 | 3.0 | 0.94 | |
| 温带季风气候 | 双差解 | -3.5 | 3.3 | -0.1 | -0.1 | 1.7 | 4.3 | 2.7 | 0.98 |
| PPP解 | -6.1 | 5.4 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 2.0 | 6.7 | 3.4 | 0.97 | |
| 亚热带季风气候 | 双差解 | -3.6 | 3.5 | -0.4 | -0.3 | 1.5 | 4.5 | 2.9 | 0.95 |
| PPP解 | -4.9 | 4.7 | -0.9 | -1.0 | 1.4 | 6.8 | 3.5 | 0.94 | |
| 热带季风气候 | 双差解 | -0.9 | 1.7 | 0.0 | -0.3 | 1.9 | 3.0 | 2.6 | 0.90 |
| PPP解 | -0.5 | 2.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 5.3 | 3.0 | 0.84 | |
| 中国区域 | 双差解 | -3.6 | 3.5 | -0.2 | -0.2 | 1.1 | 4.5 | 2.7 | 0.96 |
| PPP解 | -6.1 | 5.4 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 6.8 | 3.2 | 0.95 | |
图7 GNSS-PWV与ERA5-PWV的Bias、 RMSE区域分布(单位:mm)(a)、 (c)双差解与ERA5资料的对比结果, (b)、 (d)PPP解与ERA5资料的对比结果 Fig.7 Bias and RMSE regional distribution of GNSS-PWV and ERA5-PWV.Unit:mm.(a) and (c) the comparison results between double-difference network solution and ERA5 data, (b) and (d) the comparison results between PPP solution and ERA5 data |
5 讨论
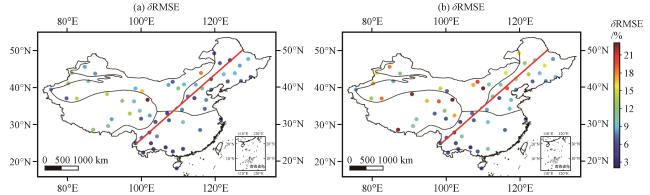
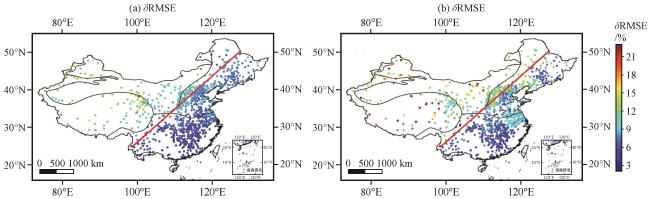
图8 GNSS-PWV与RS-PWV的δRMSE区域分布(单位:%)(a)双差解与探空资料的对比结果, (b)PPP解与探空资料的对比结果 Fig.8 Regional distribution of δ RMSE between GNSS-PWV and RS-PWV.Unit: %.(a)the comparison between double-difference network solution and radiosonde data, (b)the comparison between PPP solution and radiosonde data |